Cisco
Talos
and
the
Citizen
Lab
researchers
have
published
a
technical
analysis
of
the
powerful
Android
spyware
Predator.
Security
researchers
at
Cisco
Talos
and
the
Citizen
Lab
have
shared
technical
details
about
a
commercial
Android
spyware
named
Predator
that
is
sold
by
the
surveillance
firm
Intellexa
(formerly
known
as
Cytrox).
The
researchers
focused
their
analysis
on
two
components
of
the
mobile
spyware
implant,
respectively
tracked
as
“ALIEN”
and
“PREDATOR.”
“PREDATOR
is
an
interesting
piece
of
mercenary
spyware
that
has
been
around
since
at
least
2019,
designed
to
be
flexible
so
that
new
Python-based
modules
can
be
delivered
without
the
need
for
repeated
exploitation,
thus
making
it
especially
versatile
and
dangerous.”
reads
the
post
published
by
Cisco
Talos.
“New
analysis
from
Talos
uncovered
the
inner
workings
of
PREDATOR
and
the
mechanisms
it
uses
to
communicate
with
the
other
spyware
component
deployed
along
with
it
known
as
“ALIEN.”
Both
components
work
together
to
bypass
traditional
security
features
on
the
Android
operating
system.
Our
findings
reveal
the
extent
of
the
interweaving
of
capabilities
between
PREDATOR
and
ALIEN,
providing
proof
that
ALIEN
is
much
more
than
just
a
loader
for
PREDATOR
as
previously
thought
to
be.”
In
May
2022,
Google’s
Threat
Analysis
Group
(TAG)
researchers
discovered
three
campaigns,
between
August
and
October
2021,
targeting
Android
users
with
five
zero-day
vulnerabilities.
The
attacks
aimed
at
installing
the
surveillance
spyware
Predator,
developed
by
the
North
Macedonian
firm
Cytrox.
According
to
Google,
the
exploits
were
included
in
Cytrox’s
commercial
surveillance
spyware
that
is
sold
to
different
nation-state
actors,
including
Egypt,
Armenia,
Greece,
Madagascar,
Côte
d’Ivoire,
Serbia,
Spain,
and
Indonesia.
In
December
2021
a report published
by
CitizenLab
researchers
detailed
the
use
of
the
Predator
Spyware
against
exiled
politician
Ayman
Nour
and
the
host
of
a
popular
news
program.
The
surveillance
software
supports
common
spyware
capabilities,
such
as
recording
phone
calls,
spying
on
messaging
apps,
and
data
harvesting
on
infected
Android
devices.
Currently,
the
Predator
spyware
is
developed
and
sold
by
Israeli
company
Intellexa,
it
can
target
both
iOS
and
Android
devices.
The
surveillance
suite
offered
by
Intellexa
has
multiple
components
that
Talos
grouped
into
three
major
categories,
exploitation,
privilege
escalation,
and
malware
deployment.
The
first
two
groups
are
related
to
components
involved
in
the
exploitation
of
remote
vulnerabilities
in
the
devices
to
achieve
remote
code
execution
(RCE)
execution
followed
by
the
privilege
escalation.
“When
used
together,
these
components
provide
a
variety
of
information
stealing,
surveillance
and
remote-access
capabilities.
The
functionalities
described
here
are
just
a
subset
of
the
comprehensive
capabilities
of
the
spyware.
At
this
time,
Talos
does
not
have
access
to
all
components
of
the
spyware;
therefore,
this
capability
list
should
not
be
considered
exhaustive.”
continues
the
report.
“We
believe
that
capabilities
like
geolocation
tracking,
camera
access
or
the
ability
to
make
it
appear
as
if
the
phone
is
powering
off
may
have
been
implemented
in
the
tcore
module.”
The
researchers
reported
that
the
implant
runs
a
variety
of
processes
to
bypass
security
measured
supported
by
Android
OS.
The
malware
takes
the
“__progname”
of
the
process
that
is
currently
running
and
then
uses
it
to
decide
what
set
of
functions
to
call.
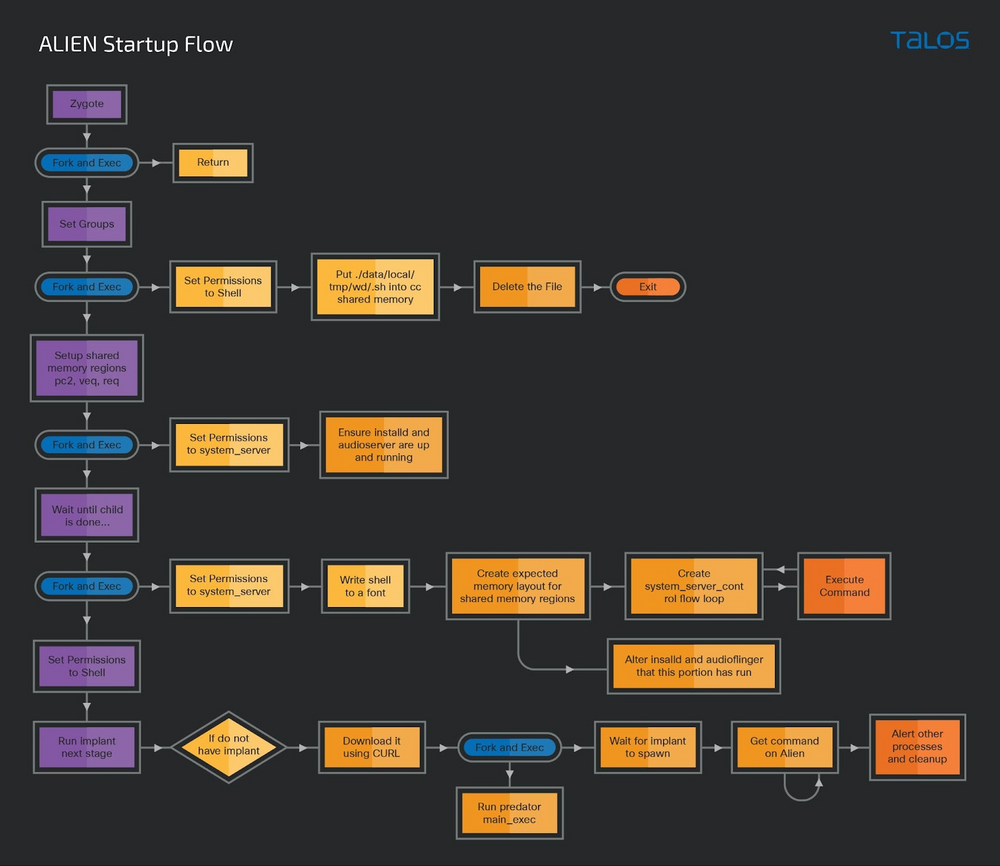
The
Alien
component
is
loaded
into
the
Android
process
named
‘zygote64,’
then
it
fetches
and
launches
additional
components,
including
the
Predator
one.
The
zygote64
and
system_server
call
chains
are
the
most
active
in
performing
tasks,
while
the
installd
call
chain
is
responsible
for
establishing
file
structures
for
other
components
of
the
spyware.
Each
of
these
call
chains
creates
a
process
structure
that
intercepts
specific
ioctl
commands,
allowing
the
spyware
to
exploit
the
SELinux
context
and
grant
different
functionalities
to
other
processes.
Alien
also
upgrades
the
existing
Predator
payload
to
a
newer
version
if
available.
Talos
experts
reported
that
ALIEN
is
not
just
a
loader,
but
it
is
also
able
to
execute
multiple
commands
issued
by
the
PREDATOR.
ALIEN
hooks
the
ioctl()
function
in
libbinder.so,
which
is
used
in
the
Android
framework
for
inter-process
communication.
“This
ioctl
hook
manages
a
variety
of
different
binder
commands,
inside
of
the
BINDER_WRITE_READ
IOCTL
command.
This
hook
filters
all
the
BINDER_WRITE_READ
functions
to
ALIEN’s
own
handler
commands.”
continues
the
analysis.
“The
commands
that
are
redirected
include
BC_TRANSACTION,
BR_TRANSACTION,
BR_REPLY,
BC_REPLY.
This
allows
the
control
of
information
into
and
out
of
the
target
process.
Within
each
of
the
selected
processes
mentioned
above,
there
are
different
actions
a
malicious
module
could
then
take
on
the
system.
This
creates
an
effective
way
to
communicate
within
the
implant
while
also
allowing
the
implant
to
hide
within
other
legitimate
system
processes.
The
implant
communicates
discreetly
with
itself,
without
network-based
indicators
and
avoiding
SELinux
restrictions.”
PREDATOR
is
the
core
component
of
the
implant,
it
is
a
pyfrozen
ELF
file
that
contains
serialized
Python
modules
and
native
code.
ALIEN
calls
the
main_exec()
function
to
launch
PREDATOR.

The
Alien
component
checks
the
device
manufacturer
name,
if
it
running
on
Samsung,
Huawei,
Oppo,
or
Xiaomi
devices,
it
iteratively
accesses
the
contents
of
directories
where
user
data
from
email,
messaging,
social
media,
and
browser
apps
are
stored.
It
also
access
It
also
enumerates
the
victim’s
list
of
contacts
and
the
user’s
media
folders,
to
access
audio,
images,
and
video
on
the
compromised
device.
The
experts
pointed
out
that
they
were
not
able
to
analyze
all
the
components
composing
the
surveillance
suite,
in
particular,
they
speculate
the
execution
of
two
additional
components.
“We
assess
with
high
confidence
that
the
spyware
has
two
additional
components
—
tcore
(main
component)
and
kmem
(privilege
escalation
mechanic)
—
but
we
were
unable
to
obtain
and
analyze
these
modules.”
concludes
the
report.
Follow
me
on
Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, spyware)