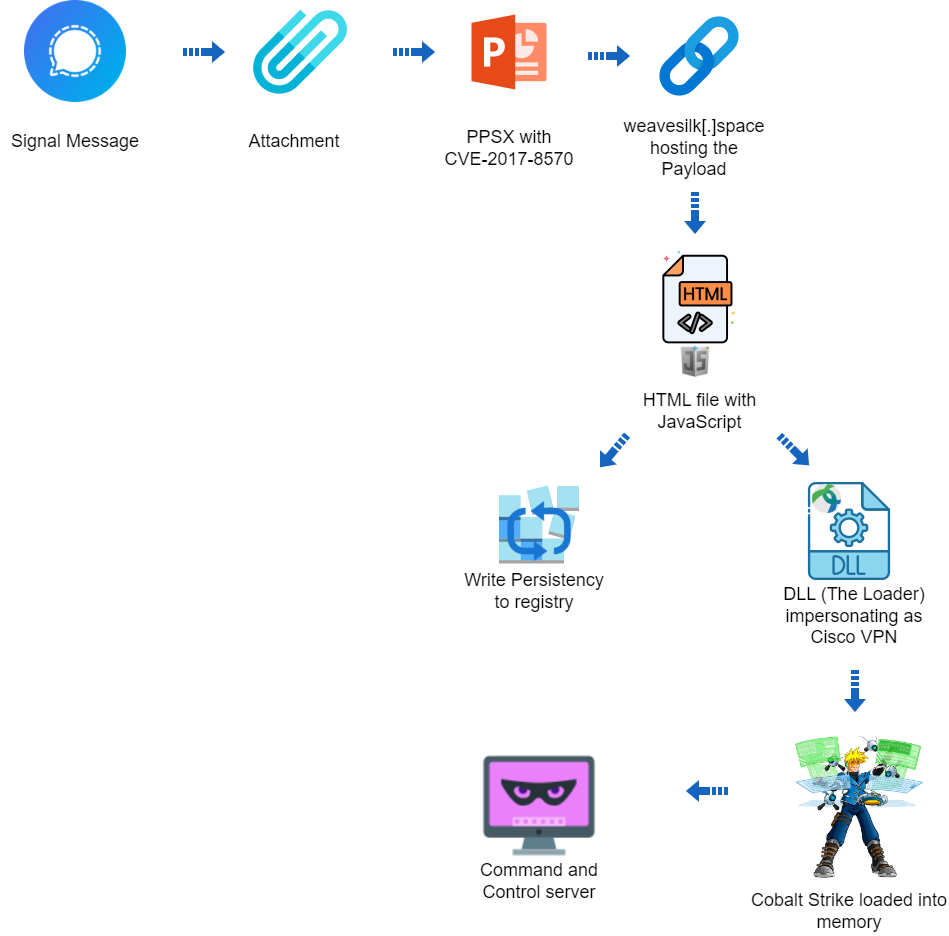
What’s happened?
Two men have been charged with hacking into computer networks in the United States, UK, other NATO countries, and Ukraine, on behalf of the Russian government.
Who are the men?
The men have been named by the US Department of Justice as Ruslan Aleksandrovich Peretyatko, who is an officer in Russia’s Federal Security Service (FSB) Center 18, and Andrey Stanislavovich Korinets.
The FSB? Isn’t that the successor to the KGB?
That’s right. The men are said to be members of the Callisto Group (also known as Star Blizzard, SEABORGIUM, TA446, COLDRIVER, TAG-53, and BlueCharlie). Callisto Group is believed to be controlled by the FSB’s 18th Centre for Information Security.
So, what are these two Russian guys alleged to have done?
The men, alongside other conspirators who as yet have not been charged, are alleged to have launched sophisticated spear-phishing campaigns to hack into victims’ computers and email accounts.
Who were they targeting?
The FSB, through the hacking activities of the Callisto Group, is believed to have been behind:
What did the spearphishing campaigns look like?
According to Microsoft, a typical attack started with an email that pretended to come from a known contact of the intended victim. Often emails were sent from a free Proton (@proton.me or @protonmail.com) account.
The initial email would usually not contain an attachment or link, but simply ask that the recipient review a document. When the intended victim responded they would be sent a new message, containing a link to a PDF on a cloud-based platform or a PDF attachment.
However, the PDF’s content would be blurred out – and a button would be displayed, asking the recipient to open the file in a cloud service such as OneDrive.
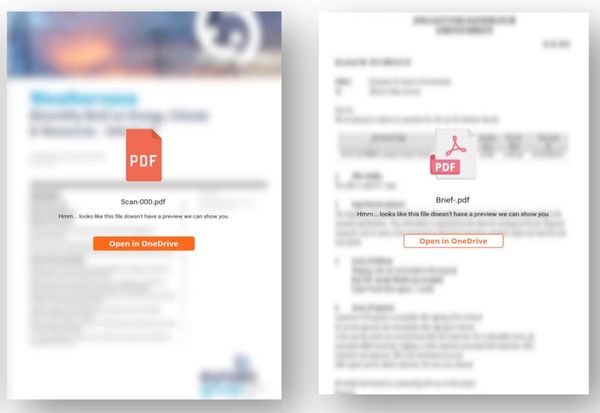
Clicking on the button, however, would take the intended victim to a phishing page which could steal their password and – if multi-factor authentication was enabled – any entered authentication token.
I guess a hardware authentication key would have been a stronger form of MFA?
That’s right. But most people don’t have any form of multi-factor authentication, let alone a hardware key.
These men have been charged by the US authorities, but how likely is it that they’ll ever appear in a US court?
Chances are that they won’t, although the US Department of State has announced rewards of up to $10 million for information which leads to the identification or location of the men, as well as their fellow conspirators.
In addition to the charges, the US and UK governments have announced sanctions against both Peretyatko and Korinets for their roles in the hacking.
The UK Government says that although some of the hacks did result in documents being leaked, “attempts to interfere with UK politics and democracy have not been successful.”
“Russia’s attempts to interfere in UK politics are completely unacceptable and seek to threaten our democratic processes. Despite their repeated efforts, they have failed,” said UK Foreign Secretary David Cameron. “In sanctioning those responsible and summoning the Russian Ambassador today, we are exposing their malign attempts at influence and shining a light on yet another example of how Russia chooses to operate on the global stage. We will continue to work together with our allies to expose Russian covert cyber activity and hold Russia to account for its actions.”