CloudBees
vulnerabilities
in
the
Jenkins
open-source
automation
server
can
be
exploited
to
achieve
code
execution
on
targeted
systems.
Researchers
from
cloud
security
firm
Aqua
discovered
a
chain
of
two
vulnerabilities
in
the
Jenkins
open-source
automation
server
that
could
lead
to
code
execution
on
targeted
systems.
Jenkins is
the
most
popular
open
source
automation
server,
it
is
maintained
by
CloudBees
and
the
Jenkins
community.
The
automation
server
supports
developers
build,
test
and
deploy
their
applications,
it
has
hundreds
of
thousands
of
active
installations
worldwide
with
more
than
1
million
users.
The
two
flaws,
tracked
as CVE-2023-27898 and CVE-2023-27905,
are
collectively
named CorePlague
impacts
Jenkins
Server
and
Update
Center.
“Exploiting
these
vulnerabilities
could
allow
an
unauthenticated
attacker
to
execute
arbitrary
code
on
the
victim’s
Jenkins
server,
potentially
leading
to
a
complete
compromise
of
the
Jenkins
server.”
reads
the
advisory
published
by
the
company.
“Furthermore,
these
vulnerabilities
could
be
exploited
even
if
the
Jenkins
server
is
not
directly
reachable
by
attackers
and
could
also
impact
self-hosted
Jenkins
servers.”

The
flaws
affect
Jenkins
servers
running
versions 2.270
through
2.393
(both
inclusive),
LTS
2.277.1 through
2.375.3
(both
inclusive) are
vulnerable.
Jenkins
Update
Centers
with
versions
below
3.15
are
vulnerable.
Aqua
researchers
reported
that
the
issues
are
related
to
how
Jenkins
processes
available
plugins,
allowing
attackers
to
conduct
attacks
such
as
cross-site
scripting
(XSS)
or
achive
remote
code
execution.
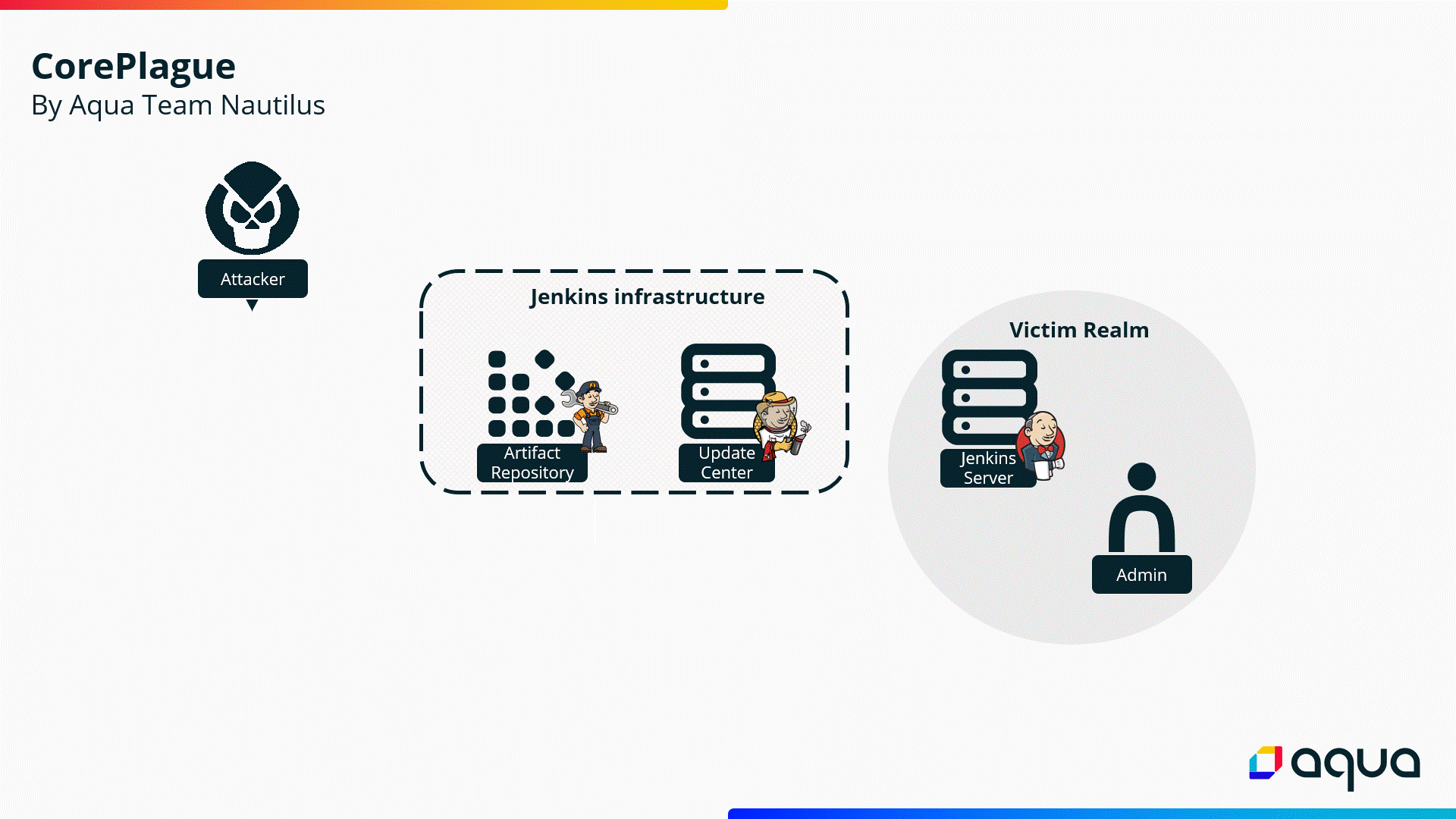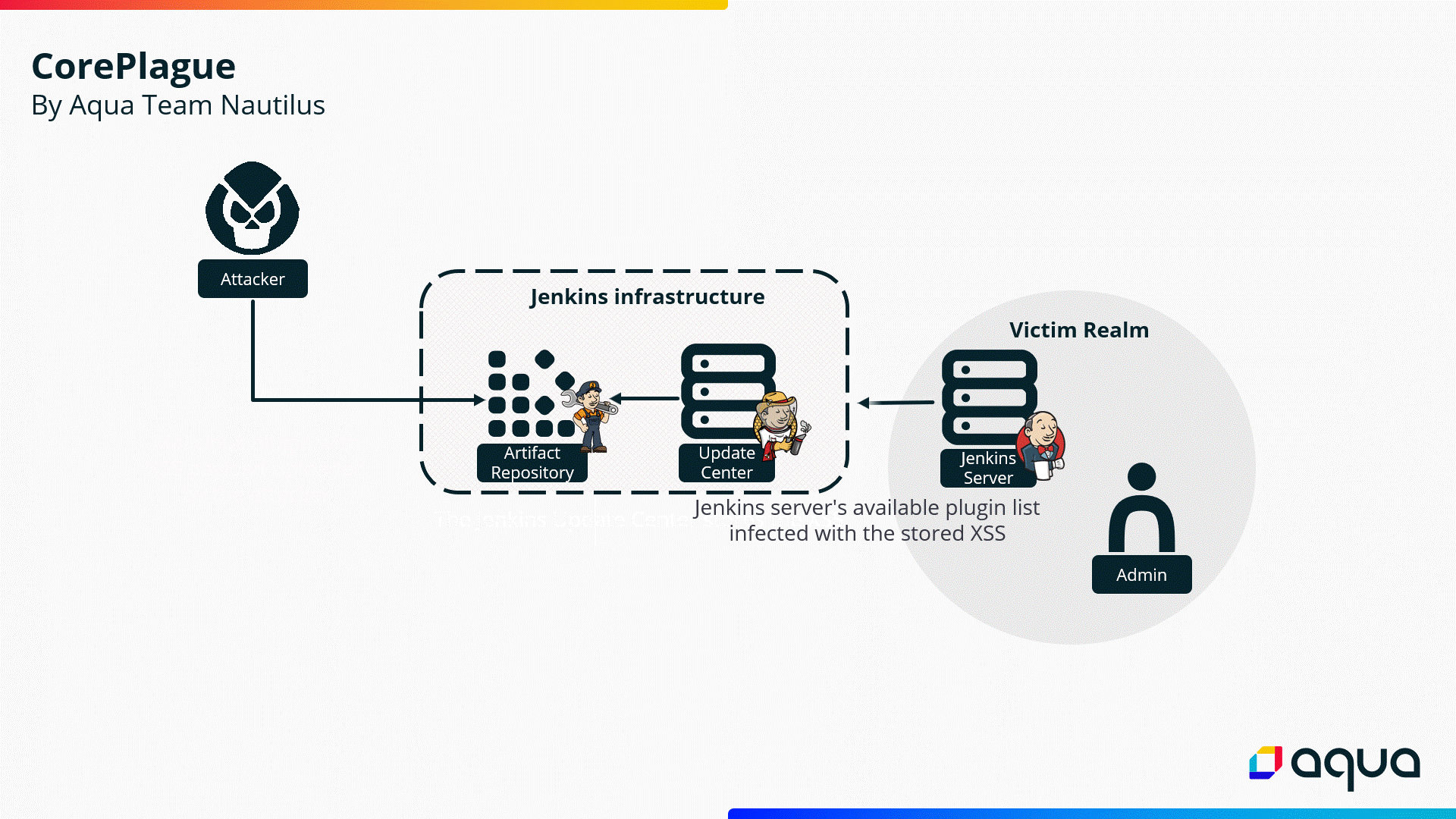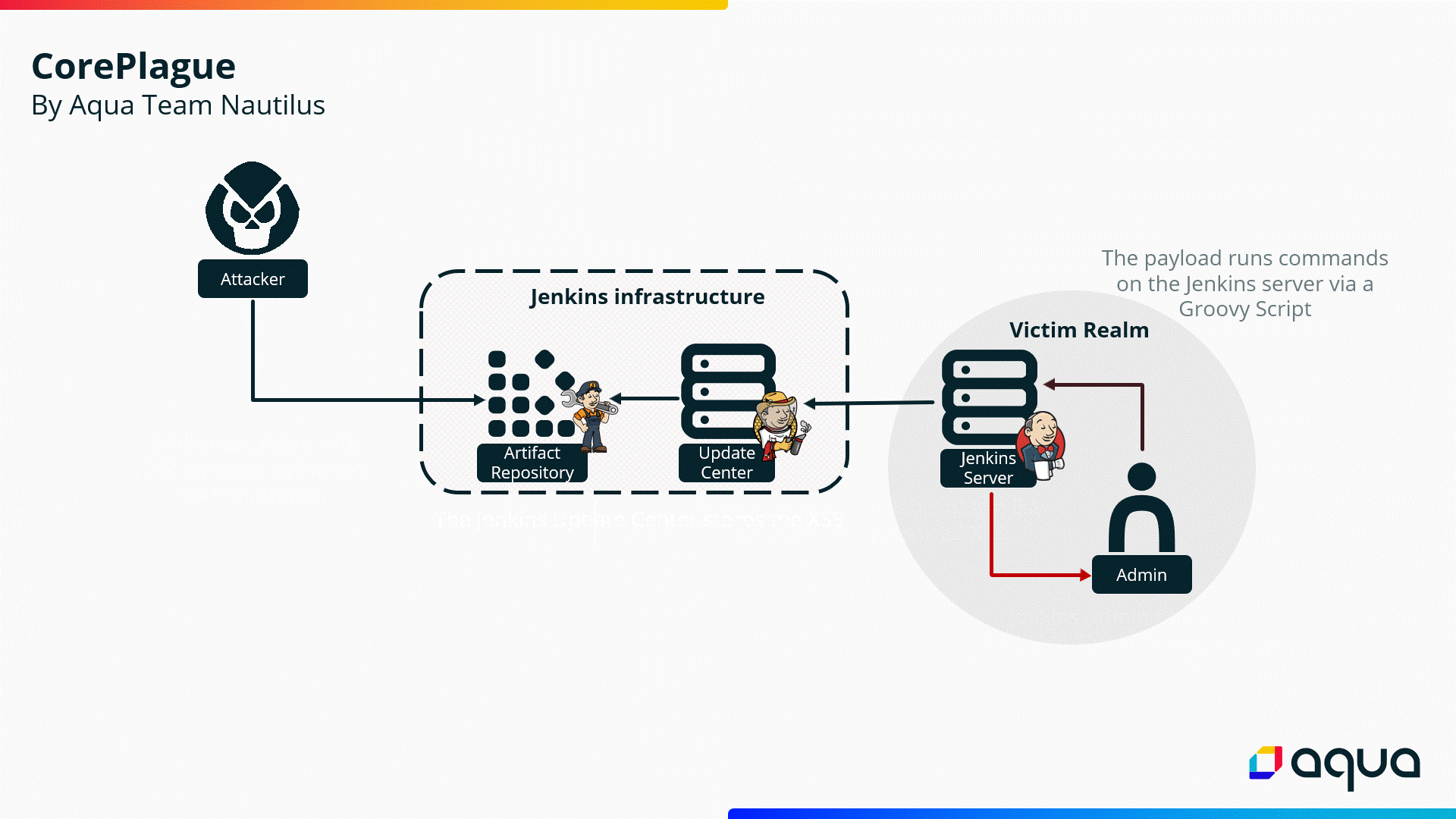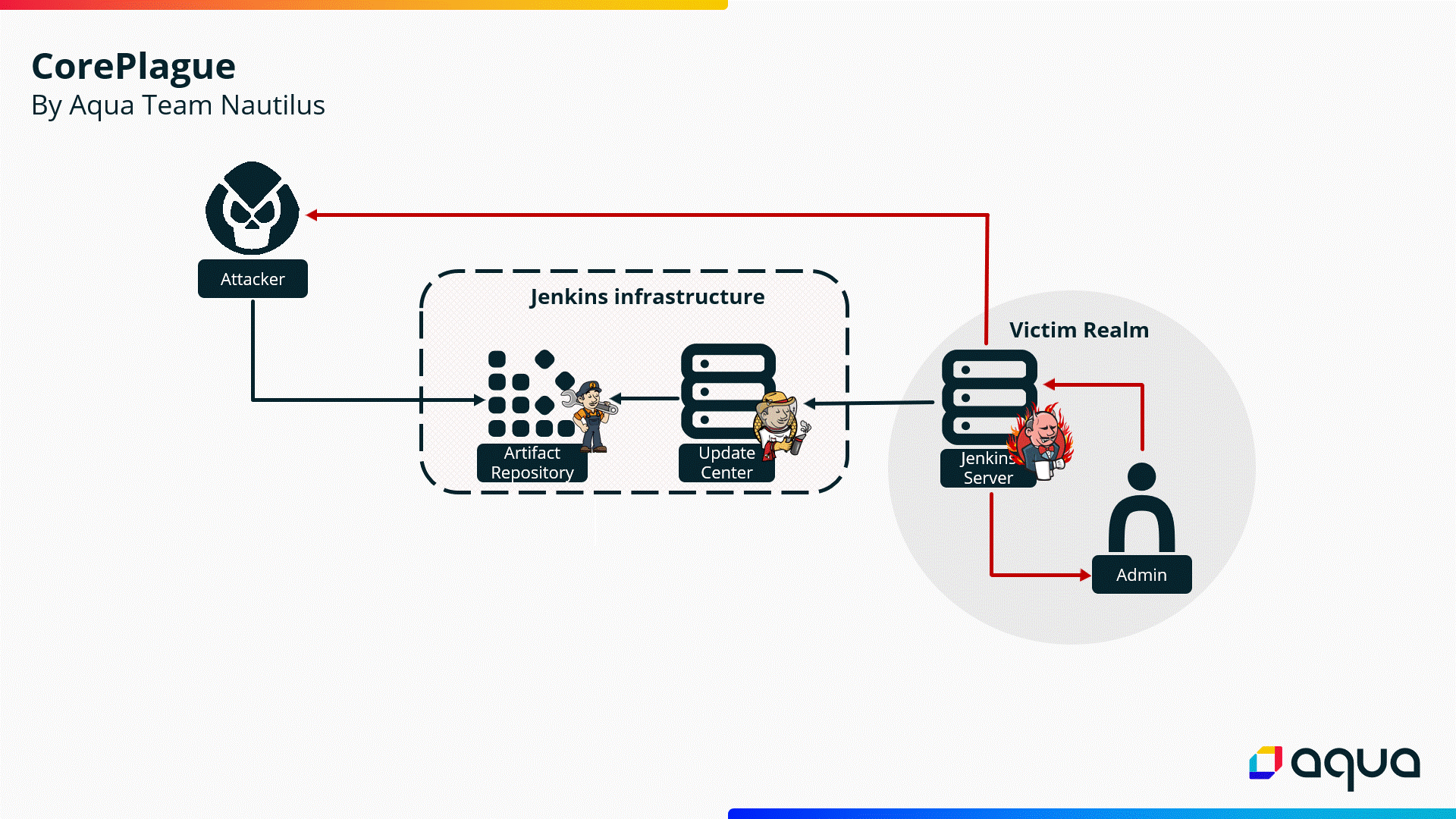
The
researchers
discovered
that
the
flaws
are
achieved
through
a
stored
XSS
exploitable
by
a
Jenkins
plugin
with
a
malicious
core
version,
which
attackers
upload
to
the Jenkins
Update
Center.
“Once
the
victim
opens
the
Available
Plugin
Manager
on
their
Jenkins
Server,
the
XSS
is
triggered,
allowing
attackers
to
run
arbitrary
code
on
the
Jenkins
Server
utilizing
the
Script
Console
API.
Importantly,
the
vulnerability
is
triggered
without
any
additional
action
from
the
victim,
and
the
exploitation
does
not
require
the
manipulated
plugin
to
be
installed.”
continues
the
advisory.
The
researchers
pointed
out
that
the
flaws
can
be
exploited
also
in
attacks
against
Jenkins
Servers
that
are
not
directly
reachable
because
the
public
Jenkins
Update
Center,
used
to
obtain
available
plugin
lists,
could
be
injected
by
attackers.
According
to
the
advisory,
in
order
to
exploit
the
flaw
the
malicious
plugin
must
be
compatible
with
the
Jenkins
server
and
it
must
be
displayed
on
the
main
page
of
the
available
plugin
feed.
“The
Jenkins
team
implemented
a
site
tiering
mechanism
to
show
only
plugins
that
are
compatible
with
the
current
Jenkins
Server,
meaning
the requiredCore version
of
the
plugin
is
older
than
the
Jenkins
Server.”
continues
the
report.
“Since
the
requiredCore
version
is
older,
the
warning
message
shown
earlier
will
not
appear,
and
the
requiredCore
value
will
not
be
processed
as
HTML,
making
it
safe
from
the
XSS.”
The
flaws
were
reported
to
the
company
on
January
2023,
and
the
Jenkins
team
acknowledged
the
t
and
issued
them
released
patches
for Update
Center and server.
Follow
me
on
Twitter:
@securityaffairs
and
Facebook
and
Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs –
hacking,
CloudBees)






%20v1.1.jpg#keepProtocol)