Today,
the
LockBit
ransomware
is
the
most
active
and
successful
cybercrime
organization
in
the
world.
Attributed
to
a
Russian
Threat
Actor,
LockBit
has
stepped
out
from
the
shadows
of
the
Conti
ransomware
group,
who
were
disbanded
in
early
2022.
LockBit
ransomware
was
first
discovered
in
September
2019
and
was
previously
known
as
ABCD
ransomware
because
of
the
“.abcd
virus”
extension
first
observed.
LockBit
operates
as
a
Ransomware-as-a-service
(RaaS)
model.
In
short,
this
means
that
affiliates
make
a
deposit
to
use
the
tool,
then
split
the
ransom
payment
with
the
LockBit
group.
It
has
been
reported
that
some
affiliates
are
receiving
a
share
as
high
of
75%.
LockBit’s
operators
have
posted
advertisements
for
their
affiliate
program
on
Russian-language
criminal
forums
stating
they
will
not
operate
in
Russia
or
any
CIS
countries,
nor
will
they
work
with
English-speaking
developers
unless
a
Russian-speaking
“guarantor”
vouches
for
them.
Initial
attack
vectors
of
LockBit
include
social
engineering,
such
as
phishing,
spear
phishing,
and
business
email
compromise
(BEC),
exploiting
public-facing
applications,
hiring
initial
access
brokers”
(IABs),
and
using
stolen
credentials
to
access
valid
accounts,
such
as
remote
desktop
protocol
(RDP),
as
well
as
brute-force
cracking
attacks.
During
last
year’s
Global
Threat
Forecast
webinar,
hosted
by
SecurityHQ,
we
identified
LockBit
as
a
significant
threat
and
highlighted
them
as
a
Threat
Actor
to
pay
close
attention
to
during
2022.
LockBit
Targets
LockBit
has
typically
focused
attacks
on
government
entities
and
enterprises
in
a
variety
of
sectors,
such
as
healthcare,
financial
services,
and
industrial
goods
and
services.
The
ransomware
has
been
observed
targeting
countries
globally,
including
the
US,
China,
India,
Indonesia,
Ukraine,
France,
the
UK,
and
Germany.
Another
interesting
feature
of
LockBit
is
that
it
is
programmed
in
a
way
that
it
cannot
be
used
in
attacks
against
Russia
or
CIS
countries
(Commonwealth
of
Independent
States).
This
is
likely
a
precautionary
measure
taken
by
the
group
to
avoid
any
potential
backlash
from
the
Russian
government.
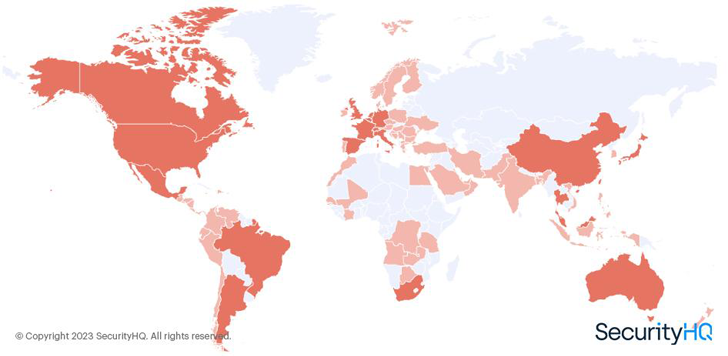
The
map
below
shows
the
locations
targeted
by
LockBit.
 |
|
Figure 1 – SecurityHQ Analysis of LockBit Victims Per Geography |
A
Busy
Year
for
LockBit
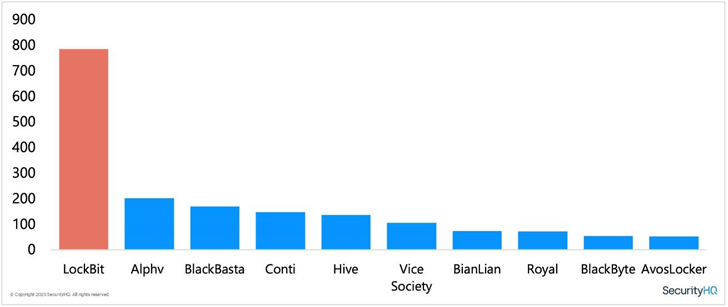
Through
analysis
of
leak
site
data,
we
were
able
to
get
a
true
picture
of
how
many
successful
attacks
LockBit
had
made.
In
2022,
the
group
published
more
successful
attacks
than
any
other
ransomware
group.
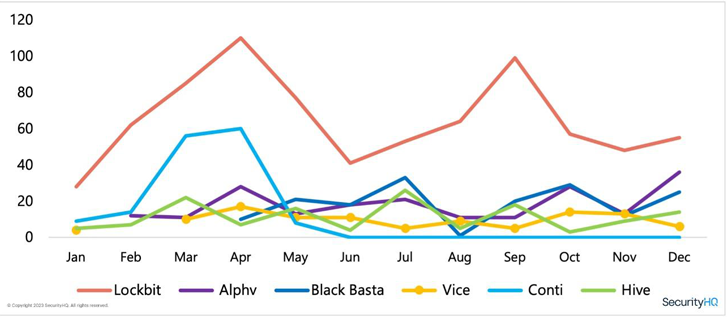
We
have
mapped
the
activity
of
LockBit
throughout
the
year
against
other
well-known
ransomware
groups.
You
can
see
the
decline
of
Conti
as
the
group
started
to
shut
down
operations.
It
is
now
reported
however,
that
members
of
the
once
prolific
Conti
ransomware
group
are
now
operating
within
the
BlackBasta,
BlackByte
and
Karakurt
ransomware
groups.
The
graph
below
demonstrates
how
active
LockBit
were
during
2022,
compared
to
other
ransomware
groups.
One
of
the
unique
features
of
LockBit
is
their
bug
bounty
program
for
their
ransomware
builders
and
compilers.
The
group
offers
a
$1
million
reward
for
anyone
who
can
dox
(publicly
reveal
the
identities
of)
their
owners.
This
is
a
significant
sum,
and
it
shows
how
serious
LockBit
is
about
maintaining
their
anonymity.
Recently,
the
group
has
been
linked
to
an
attack
on
Royal
Mail
in
the
UK.
However,
LockBit
has
denied
any
involvement
in
the
attack,
stating
that
it
was
carried
out
by
an
affiliate.
This
is
not
uncommon
for
ransomware
groups,
as
they
often
use
affiliates
to
carry
out
attacks
in
order
to
distance
themselves
from
the
consequences.
Overall,
the
LockBit
ransomware
group
is
a
formidable
and
sophisticated
cybercrime
organization
that
poses
a
significant
threat
to
businesses
and
organizations
around
the
world.
With
a
well-established
ransomware-as-a-service
model,
a
bug
bounty
program,
and
a
willingness
to
reward
those
who
reveal
their
identities,
LockBit
is
a
force
to
be
reckoned
with
in
the
threat
landscape.
What
is
RaaS?
Ransomware-as-a-service
(RaaS)
has
gained
popularity
in
recent
years.
RaaS
refers
to
a
type
of
business
model
where
ransomware
operators
provide
the
malware
and
tools
to
other
individuals
or
organised
crime
groups
to
carry
out
ransomware
attacks,
in
exchange
for
a
share
of
the
ransom
payment.
This
allows
even
less
technically
skilled
individuals
to
participate
in
ransomware
attacks,
increasing
the
number
of
attacks
and
making
it
more
difficult
to
track
and
apprehend
the
attackers.
What
to
Do
Next
To
enhance
your
security
posture,
it
is
recommended
that
businesses
do
the
following
steps:
-
Ensure
Managed
Detection
and
Response
(MDR)
is
used
to
understand
malicious
or
anomalous
activity,
analyse,
prioritise,
and
respond
to
threats
in
rapid
time,
and
safeguard
your
data,
people
and
processes. -
Ensure
that
employees
are
trained
and
educated
on
the
latest
cyber
security
threats,
so
that
they
know
how
to
spot
an
attack,
and
respond
to
it
in
the
right
way.
To
listen
to
SecurityHQ
experts
discuss
some
of
the
greatest
threats
seen
throughout
2022,
discuss
the
consequences
of
a
breach,
with
predictions
for
2023,
and
how
to
mitigate
against
upcoming
cyber
security
threats,
download
this
webinar
recording’
Global
Threat
Landscape
2023
Forecast‘,
to
know
more.
Note:
This
article
is
by
Aaron
Hambleton,
Director
for
Middle
East
&
Africa
at
SecurityHQ.
With
over
11
years
of
experience
across
various
sectors
like
Financial
Services,
Retail,
Insurance,
Government,
and
Telecommunications,
Aaron
is
a
certified
GCDA
and
has
expertise
in
incident
response,
threat
hunting,
vulnerability
management,
cyber
security
operations,
threat
intelligence,
and
consultancy.
this
article
interesting?
Follow
us
on
and
to
read
more
exclusive
content
we
post.