Robust April Security Patch Tuesday unveils 135 Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs)

Microsoft dropped a total of 135 fixes across 19 product families on Tuesday. Out of these updates, ten deal with remote code execution bugs marked as Critical by Microsoft. Moreover, 18 vulnerabilities have obtained a CVSS base score of 8.0 or higher. There is an under active exploitation elevation of privilege problem in the Windows Common Log File system driver categorized as Important.
Upon patch implementation, Microsoft anticipates 11 additional CVEs to be more susceptible to exploitation within the next 30 days. Some of this month’s vulnerabilities can be directly identified through Sophos protections, and all relevant information can be found in the provided table below.
Besides the mentioned patches, there are sixteen Adobe Reader bugs of Important severity affecting ColdFusion included in this release. These are detailed in the attached Appendix D. We have also integrated all Edge-related CVEs into our overall statistics this month, although these patches were largely issued separately from today’s update.
For detailed coverage, we have appended sections listing all Microsoft patches arranged by severity, exploit likelihood timeline, CVSS Base score, and product family. There is also a specific appendix concentrating on advisory-style updates, and a segmentation of patches impacting the supported Windows Server platforms.
Statistical Overview
- Total CVEs: 135
- Publicly disclosed: 0
- Exploit discovered: 1
- Severity
- Critical: 10
- Important: 114
- Low: 2
- High / Medium / Low: 9 (CVEs related to Edge through Chromium; see Appendix C)
- Impact
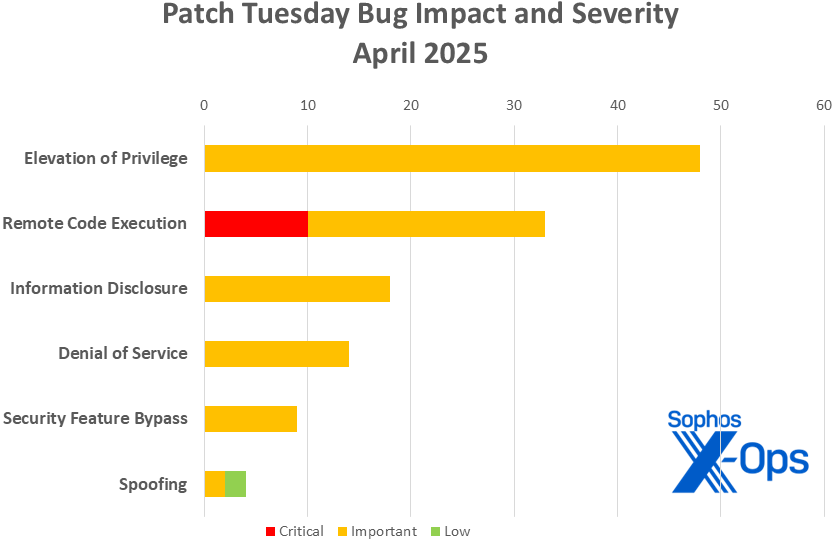
- Elevation of Privilege: 48
- Remote Code Execution: 33
- Information Disclosure: 18
- Denial of Service: 14
- Security Feature Bypass: 9
- Spoofing: 4
- Unknown: 9 (CVEs related to Edge through Chromium; see Appendix C)
- CVSS score 9.0 or higher: 0
- CVSS base score 8.0 or higher: 18
Presentation 1: Elevation of privilege bugs make up more than 33% of all April patches, while Critical-severity flaws exclusively pertain to remote code execution issues. (Please take note that nine of the Edge updates discussed in this release lack full impact data and use a distinct severity classification, hence they are not shown in this chart; refer to Appendix C for more details)
Products
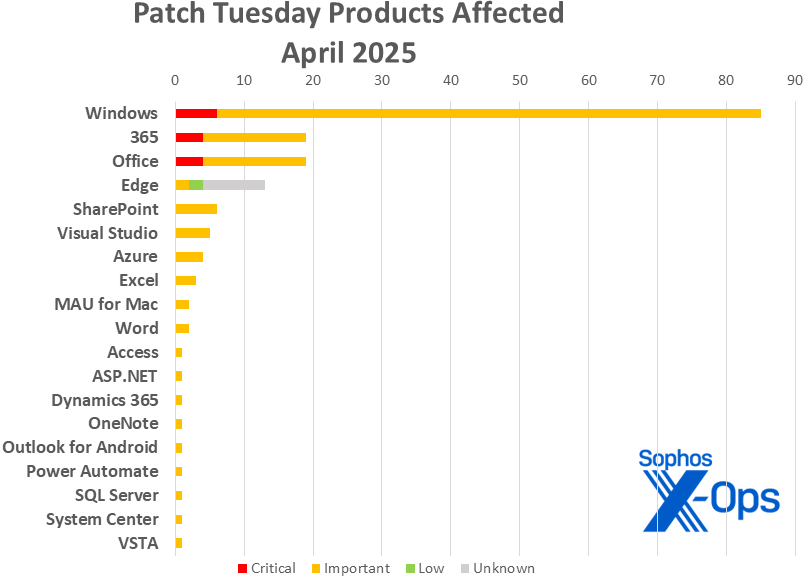
- Windows: 89
- 365: 15
- Office: 15
- Edge: 13
- SharePoint: 6
- Visual Studio: 5
- Azure: 4
- Excel: 3
- Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU) for Mac: 2
- Word: 2
- Access: 1
- ASP.NET: 1
- Dynamics 365: 1
- OneNote: 1
- Outlook for Android: 1
- Power Automate for Desktop: 1
- SQL Server: 1
- System Center: 1
- Visual Studio Tools for Applications (VSTA): 1
Consistent with our methodology, CVEs applicable to multiple product families are counted once for each affected family. It’s important to note that CVE labels in April may not accurately reflect the impacted product families. Specifically, some CVEs references in the Office category might list products that are not present in the product roster affected by the CVE, and vice versa.
Figure 2: Nineteen product families undergo implications of the April patches; as mentioned earlier, nine Edge updates analyzed in this report lack detailed impact breakdown and adhere to a disparate severity hierarchy, therefore appearing as “unknown” in impact; further information can be found in Appendix C
Standout April Enhancements
Beyond the previously addressed concerns, numerous specific occurrences warrant special attention.
CVE-2025-26642, CVE-2025-27745, CVE-2025-27747, CVE-2025-27748, CVE-2025-27749, CVE-2025-27750, CVE-2025-27751, CVE-2025-2772, CVE-2025-29791, CVE-2025-29816, CVE-2025-29820, CVE-2025-29822 (12 CVEs) – assorted Office dilemmas
The Office suite is bombarded with a heavy patch load this month, particularly unnerving for users of Office LTSC for Mac between 2021 and 2024. All 12 CVEs listed above pertain to these editions, but the patches are not yet available; impacted users should monitor the CVEs for any update releases. To exacerbate matters, five out of the twelve (CVE-2025-27745, CVE-2025-27748, CVE-2025-27749, CVE-2025-27752, CVE-2025-29791) involve the Preview Pane as an exploit vector, upgrading four from Important to Critical severity.
CVE-2025-26647 — Windows Kerberos Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
This elevation of privilege issue with an Important severity seems to hinge on the attacker’s ability to compromise a trusted Certificate Authority. Should an attacker succeed, The intruder has the capability to perform this action and then generate a certificate with a specified Subject Key Identifier (SKI) value. Subsequently, this certificate could be utilized to establish a connection with the system, ultimately taking on the identity of any account. This presents recommended measures, such as ensuring all Windows machines and domain controllers are updated with the latest patch, monitoring audit events to detect any machine or device that may have missed the update, and activating Enforcement Mode once certificates issued by unrecognized authorities are no longer used in your environment. An issue with CA compromise has long persisted in the ecosystem; given that Microsoft has identified this CVE as more susceptible to exploitation in the next 30 days, it should be prioritized in your setup.
CVE-2025-27743 — Microsoft System Center Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
An elevation-of-privilege problem deemed significant, this CVE impacts a range of System Center products (Operations Manager, Service Manager, Orchestrator, Data Protection Manager, Virtual Machine Manager) and affects users who repurpose existing System Center .exe installer files to deploy new instances in their setups. The root of the issue lies in an untrusted search path within System Center, which could potentially allow an attacker, with authorized access and expertise in DLL hijacking, to elevate their privileges. Microsoft’s recommendation for affected users is to delete their current installer setup files (.exe) and then download the most recent version of the respective System Center product (.ZIP).
CVE-2025-29809 — Windows Kerberos Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
Another concern that may demand special attention from administrators, this security feature bypass with significant severity necessitates the reversal of a previous policy. According to Microsoft’s advice, “The policy outlined in Guidance for blocking rollback of Virtualization-based Security (VBS) related security updates has been revised to incorporate the latest modifications. If you have deployed this policy, you will need to redeploy using the updated policy.”
Furthermore, for those who may have overlooked the announcement, Microsoft has decided to postpone the deprecation of driver update synchronization via WSUS (Windows Server Update Services) from their previous plans. Individuals still reliant on this service (especially for “disconnected” devices) have been granted an extension for now, but should continue preparing for the transition to the cloud-based services that Microsoft currently emphasizes.

Figure 3: Following last month’s remote code execution, the number of elevation of privilege issues has exceeded 100 CVEs in this month’s Patch Tuesday release
Sophos protections
| CVE | Sophos Intercept X/Endpoint IPS | Sophos XGS Firewall |
| CVE-2025-27482 | Exp/2527482-A | Exp/2527482-A |
| CVE-2025-29792 | Exp/2529792-A | Exp/2529792-A |
| CVE-2025-29812 | Exp/2529812-A | Exp/2529812-A |
| CVE-2025-29812 | Exp/2529812-A | Exp/2529812-A |
As is the case every month, if you prefer not to wait for your system to automatically fetch Microsoft’s updates, you have the option to manually download them from the Windows Update Catalog website. Run the **winver.exe** tool to identify the Windows 10 or 11 build you are using, and then download the Cumulative Update package tailored to your system’s architecture and build number.
Appendix A: Vulnerability Impact and Severity
This is an April patch list organized by impact and then further sorted by severity, with each list arranged by CVE.
Elevation of Privilege (48 CVEs)
| **Important severity** | |
| CVE-2025-20570 | Visual Studio Code Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-21191 | Windows Local Security Authority (LSA) Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-21204 | Windows Process Activation Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-24058 | Windows DWM Core Library Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-24060 | Microsoft DWM Core Library Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-24062 | Microsoft DWM Core Library Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-24073 | Microsoft DWM Core Library Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-24074 | Microsoft DWM Core Library Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26639 | Windows USB Print Driver Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26640 | Windows Digital Media Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26648 | Windows Kernel Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26649 | Windows Secure Channel Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26665 | Windows upnphost.dll Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26675 | Windows Subsystem for Linux Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26679 | RPC Endpoint Mapper Service Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26681 | Win32k Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26687 | Win32k Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-26688 | Microsoft Virtual Hard Disk Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27467 | Windows Digital Media Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27475 | Windows Update Stack Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27476 | Windows Digital Media Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27478 | Windows Local Security Authority (LSA) Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27483 | NTFS Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27484 | Windows Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) Device Host Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27489 | Azure Local Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27490 | Windows Bluetooth Service Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27492 | Windows Secure Channel Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27727 | Windows Installer Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27728 | Windows Kernel-Mode Driver Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| CVE-2025-27730 | Windows Digital Media Vulnerability Leading to Higher Privileges |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-27731 | Vulnerability in Microsoft OpenSSH for Windows leading to Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-27732 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Graphics Component |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-27733 | Vulnerability in NTFS leading to Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-27739 | Windows Kernel Vulnerability causing Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-27740 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Active Directory Certificate Services |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-27741 | NTFS Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-27743 | Vulnerability in Microsoft System Center leading to Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-27744 | Microsoft Office Vulnerability causing Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29792 | Microsoft Office Vulnerability leading to Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29800 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU) |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29801 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU) |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29802 | Visual Studio Vulnerability causing Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29803 | Vulnerability in Visual Studio Tools for Applications and SQL Server Management Studio leading to Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29804 | Visual Studio Vulnerability causing Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29810 | Active Directory Domain Services Vulnerability causing Privilege Elevation |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29811 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Mobile Broadband Driver |
| Security Issue: CVE-2025-29812 | Vulnerability in DirectX Graphics Kernel causing Privilege Elevation |
Execution of Code Remotely (33 CVEs)
| Severity Level: Critical | |
| CVE-2025-26663 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) |
| CVE-2025-26670 | Vulnerability in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Client leading to Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-26686 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows TCP/IP |
| CVE-2025-27480 | Vulnerability in Windows Remote Desktop Services leading to Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27482 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows Remote Desktop Services |
| CVE-2025-27491 | Windows Hyper-V Vulnerability causing Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27745 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| CVE-2025-27748 | Microsoft Office Vulnerability causing Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27749 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| CVE-2025-27752 | Critical flaw found in Microsoft Excel for Remote Code Execution |
| Urgent severity level | |
| CVE-2025-21205 | Window telephone service vulnerability for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-21221 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows Telephony Service |
| CVE-2025-21222 | Windows Telephony Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-25000 | Critical vulnerability in Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-26642 | Vulnerability in Microsoft Office could lead to Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-26666 | Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Windows Media Service |
| CVE-2025-26668 | Windows RRAS Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-26671 | Windows Remote Desktop Services vulnerability leading to Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-26674 | Critical flaw in Windows Media Service for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27477 | Exploit found in Windows Telephony Service for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27481 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows Telephony Service |
| CVE-2025-27487 | Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Remote Desktop Client |
| CVE-2025-27729 | Vulnerability in Windows Shell for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27746 | Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| CVE-2025-27747 | Vulnerability in Microsoft Word could lead to Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27750 | Critical exploit discovered in Microsoft Excel for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27751 | Critical vulnerability in Microsoft Excel for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-29791 | Exploit in Microsoft Excel leading to Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-29793 | Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint |
| CVE-2025-29794 | Vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint could lead to Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-29815 | Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) vulnerability for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-29820 | Vulnerability in Microsoft Word leading to Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-29823 | Critical Microsoft Excel flaw for Remote Code Execution discovered |
Data Leakage (18 CVEs)
| Urgent severity level | |
| CVE-2025-21197 | Critical vulnerability in Windows NTFS resulting in Data Disclosure |
| CVE-2025-21203 | Information Leakage vulnerability in Windows RRAS detected for exploitation |
| CVE-2025-25002 | Azure Local Cluster Data Leakage vulnerability identified |
| CVE-2025-26628 | Azure Local Cluster Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26664 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26667 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26669 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26672 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26676 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27474 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27736 | Windows Power Dependency Coordinator Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27738 | Windows Resilient File System (ReFS) Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27742 | NTFS Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29805 | Outlook for Android Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29808 | Windows Cryptographic Services Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29817 | Microsoft Power Automate Desktop Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29819 | Windows Admin Center in Azure Portal Data Exposure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29821 | Microsoft Dynamics Business Central Data Exposure Weakness |
Service Unavailability (14 CVEs)
| Significant seriousness | |
| CVE-2025-21174 | Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26641 | Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26651 | Windows Local Session Manager (LSM) Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26652 | Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26673 | Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26680 | Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26682 | ASP.NET Core and Visual Studio Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27469 | Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27470 | Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27471 | Microsoft Streaming Service Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27473 | HTTP.sys Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27479 | Kerberos Key Distribution Proxy Service Service Unavailability Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27485 | Windows Standard-Based Storage Management Service Denial of Service Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27486 | Windows Standard-Based Storage Management Service Vulnerability to Denial of Service |
Security Element Bypass (9 CVEs)
| Critical level of concern | |
| CVE-2025-26635 | Windows Greetings System Element Bypass Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26637 | BitLocker Security Feature Circumvention Flaw |
| CVE-2025-26678 | Windows Defender Application Control Security Feature Bypass Condition |
| CVE-2025-27472 | Windows Indication of the Web Safety Feature Bypass Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27735 | Windows Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) Security Element Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-27737 | Windows Security Zone Mapping Security Element Bypass Bug |
| CVE-2025-29809 | Windows Kerberos Security Element Bypass Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29816 | Microsoft Word Security Element Bypass Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29822 | Microsoft OneNote Security Element Bypass Weakness |
Impersonation (4 CVE)
| Critical level of concern | |
| CVE-2025-26644 | Windows Greetings Impersonation Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26647 | Windows Kerberos Elevation of Rights Weakness |
| CVE-2025-25001 | Microsoft Edge for iOS Impersonation Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29796 | Microsoft Edge for iOS Impersonation Weakness |
Appendix B: Vulnerability to Exploitation and CVSS
Below is an assortment of the April CVEs evaluated by Microsoft to be either already exploited in the wild or more prone to exploitation in the wild within the first month following release. The listing is additionally sorted by CVE.
| Detection of Exploitation | |
| CVE-2025-29824 | Windows Mutual Log File System Driver Elevation of Rights Weakness |
| More Probable Exploitation in the Upcoming 30 Days | |
| CVE-2025-26663 | Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Vulnerability for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-26670 | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Client Vulnerability for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27472 | Windows Indication of the Web Safety Feature Bypass Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27480 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Vulnerability for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27482 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Vulnerability for Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-27727 | Windows Installer Elevation of Rights Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29792 | Microsoft Office Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-29793 | Microsoft SharePoint Vulnerability in Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2025-29794 | Microsoft SharePoint Remote Code Execution Bug |
| CVE-2025-29809 | Windows Kerberos Vulnerability in Security Feature Bypass |
| CVE-2025-29812 | DirectX Graphics Kernel Privilage Boosting Vulnerability |
The following is a selection of April’s Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) with a Microsoft-tested CVSS Base score of 8.0 or higher. They are categorized by score and additionally sorted by CVE. For more details on CVSS, refer to our collection on patch prioritization structure.
| CVSS Base | CVSS Temporal | CVE | Title |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-21205 | Windows Telephony Service Bug in Remote Code Execution |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-21221 | Windows Telephony Service Vulnerability in Remote Code Execution |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-21222 | Windows Telephony Service Execution Vulnerability in Remote Code |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-25000 | Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Code Execution Vulnerability in Remote |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-26669 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service Disclosure of Information Bug |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-27477 | Windows Telephony Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-27481 | Windows Telephony Service Code Execution Vulnerability in Remote |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-27740 | Active Directory Certificate Services Privilage Elevation Bug |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2025-29794 | Microsoft SharePoint Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 8.6 | 7.5 | CVE-2025-27737 | Windows Security Zone Mapping Bug in Security Feature Bypass |
| 8.4 | 7.3 | CVE-2025-26678 | Windows Defender Application Control Bug in Security Feature Bypass |
| 8.1 | 7.1 | CVE-2025-26647 | Windows Kerberos Vulnerability in Privilage Elevation |
| 8.1 | 7.1 | CVE-2025-26663 | Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| 8.1 | 7.1 | CVE-2025-26670 | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Client Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| 8.1 | 7.1 | CVE-2025-26671 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| 8.1 | 7.1 | CVE-2025-27480 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| 8.1 | 7.1 | CVE-2025-27482 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| 8.0 | 7.0 | CVE-2025-27487 | Remote Desktop Client Remote Code Execution Weakness |
Appendix C: Products Impacted
Below is a list of patches for April categorized by product line, then organized by seriousness. Every list is additionally grouped by CVE. Patches that pertain to multiple product lines are displayed repeatedly, once for each product family. Concerns that impact Windows Server are further detailed in Appendix E.
Windows (89 CVEs)
| Seriousness of high level | |
| CVE-2025-26663 | Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26670 | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Client Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26686 | Windows TCP/IP Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27480 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27482 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27491 | Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| Significant seriousness | |
| CVE-2025-21174 | Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service Denial of Service Weakness |
| CVE-2025-21191 | Windows Local Security Authority (LSA) Elevation of Advantage Weakness |
| CVE-2025-21197 | Windows NTFS Information Disclosure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-21203 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Information Disclosure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-21204 | Windows Process Activation Elevation of Advantage Weakness |
| CVE-2025-21205 | Windows Telephony Service Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-21221 | Exploit for Unauthorized Code Execution in Windows Telephony Service |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-21222 | Risk of Unauthorized Code Execution in Windows Telephony Service |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-24058 | Potential Elevation of Privileges in Windows DWM Core Library |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-24060 | Possible Privilege Escalation in Microsoft DWM Core Library |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-24062 | Vulnerability Found: Microsoft DWM Core Library Privilege Elevation |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-24073 | Risk of Privilege Escalation in Microsoft DWM Core Library |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-24074 | Security Flaw: Elevation of Privilege in Microsoft DWM Core Library |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26635 | Possible Bypass of Windows Hello Security Feature |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26637 | Risk of Bypassing BitLocker Security Feature |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26639 | Potential Privilege Escalation in Windows USB Print Driver |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26640 | Risk of Privilege Escalation in Windows Digital Media Services |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26641 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26644 | Potential Windows Hello Spoofing Vulnerability Detected |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26647 | Risk of Privilege Escalation in Windows Kerberos System |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26648 | Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability Found in Windows Kernel |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26649 | Privilege Escalation Issue in Windows Secure Channel Services |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26651 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Windows Local Session Manager (LSM) |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26652 | Service Disruption Vulnerability in Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26664 | Risk of Information Disclosure in Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26665 | Potential Privilege Escalation in Windows upnphost.dll Service |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26666 | Risk of Remote Code Execution in Windows Media Services |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26667 | Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26668 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability Detected in Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26669 | Data Breach Risk in Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26671 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows Remote Desktop Services |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26672 | Risk of Information Disclosure in Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26673 | Potential Denial of Service in Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26674 | Vulnerability Detected: Remote Code Execution in Windows Media Services |
| Security Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26675 | Security Vulnerability of Elevated Privileges in Windows Subsystem for Linux |
| CVE-2025-26676 | Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) |
| CVE-2025-26678 | Bypass Vulnerability in Security Feature of Windows Defender Application Control |
| CVE-2025-26679 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in RPC Endpoint Mapper Service |
| CVE-2025-26680 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service |
| CVE-2025-26681 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Win32k |
| CVE-2025-26687 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Win32k |
| CVE-2025-26688 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Microsoft Virtual Hard Disk |
| CVE-2025-27467 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Digital Media |
| CVE-2025-27469 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) |
| CVE-2025-27470 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service |
| CVE-2025-27471 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Microsoft Streaming Service |
| CVE-2025-27472 | Bypass Vulnerability in Security Feature of Windows Mark of the Web |
| CVE-2025-27473 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in HTTP.sys |
| CVE-2025-27474 | Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) |
| CVE-2025-27475 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Update Stack |
| CVE-2025-27476 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Digital Media |
| CVE-2025-27477 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows Telephony Service |
| CVE-2025-27478 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Local Security Authority (LSA) |
| CVE-2025-27479 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Kerberos Key Distribution Proxy Service |
| CVE-2025-27481 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Windows Telephony Service |
| CVE-2025-27483 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in NTFS |
| CVE-2025-27484 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) Device Host |
| CVE-2025-27485 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service |
| CVE-2025-27486 | Denial of Service Vulnerability in Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service |
| CVE-2025-27487 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Remote Desktop Client |
| CVE-2025-27490 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Bluetooth Service |
| CVE-2025-27492 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Secure Channel |
| CVE-2025-27727 | Privilege Elevation Vulnerability in Windows Installer |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27728 | Privilege Escalation Bug in Windows Kernel-Mode Driver |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27729 | Windows Shell Security Flaw Allows Remote Code Execution |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27730 | Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability in Windows Digital Media |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27731 | Windows OpenSSH Elevation of Privilege Bug |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27732 | Windows Graphics Component Vulnerability Enables Privilege Escalation |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27733 | Privilege Escalation Bug in NTFS System |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27735 | Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability in Windows Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27736 | Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Windows Power Dependency Coordinator |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27737 | Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability in Windows Security Zone Mapping |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27738 | Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Windows Resilient File System (ReFS) |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27739 | Privilege Escalation Bug in Windows Kernel Process |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27740 | Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability in Active Directory Certificate Services |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27741 | Privilege Escalation Bug in NTFS System |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27742 | Information Disclosure Vulnerability in NTFS System |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29808 | Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Windows Cryptographic Services |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29809 | Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability in Windows Kerberos |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29810 | Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability in Active Directory Domain Services |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29811 | Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability in Windows Mobile Broadband Driver |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29812 | Privilege Escalation Bug in DirectX Graphics Kernel |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29824 | Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Windows Common Log File System Driver |
A total of 365 issues were identified, including 15 CVEs
| Critical vulnerabilities | |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27745 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27748 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27749 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27752 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Excel |
| Important vulnerabilities | |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26642 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27746 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27747 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Word |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27750 | Critical |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27751 | Critical |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29791 | Critical |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29792 | High Severity |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29816 | Security Issue in Microsoft Word |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29820 | Critical Vulnerability in Microsoft Word |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29822 | Issue in Microsoft OneNote |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29823 | Critical Risk in Microsoft Excel |
Office (15 Vulnerabilities)
| Urgent situation | |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27745 | Risk in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27748 | Issue in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27749 | Critical Office Vulnerability |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27752 | High Severity Issue in Microsoft Excel |
| Significant threat | |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26642 | Security Risk in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26687 | Elevation of Privileges in Win32k |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27744 | Security Flaw in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27746 | Critical Risk in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27747 | High Severity Vulnerability in Microsoft Word |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27750 | Excel Vulnerability in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-27751 | Excel Issue in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29792 | Privilege Elevation Issue in Microsoft Office |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29816 | Security Bypass Vulnerability in Microsoft Word |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29820 | Critical Excel Vulnerability in Microsoft Word |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29822 | Security Bypass Issue in Microsoft OneNote |
Edge (13 Vulnerabilities)
| High Risk | |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-25000 | Remote Code Execution Issue in Microsoft Edge |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-29815 | Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Edge |
| Low-Level Risk | |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-25001 | Spoofing Vulnerability in Microsoft Edge for iOS |
Weakness
SharePoint (6 Weaknesses)
| Essential seriousness | |
| CVE-2025-26642 | Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27746 | Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27747 | Microsoft Word Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29793 | Microsoft SharePoint Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29794 | Microsoft SharePoint Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29820 | Microsoft Word Remote Code Execution Weakness |
Visual Studio (5 Weaknesses)
| Essential seriousness | |
| CVE-2025-20570 | Visual Studio Code Elevation of Privilege Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26682 | ASP.NET Core and Visual Studio Denial of Service Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29802 | Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Weakness |
| CVE-2025-29804 | Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Weakness |
Azure (4 Weaknesses)
| Essential seriousness | |
| CVE-2025-25002 | Azure Local Cluster Information Disclosure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-26628 | Azure Local Cluster Information Disclosure Weakness |
| CVE-2025-27489 | Azure Local Cluster Information Disclosure Weakness | Azure Local Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-29819 | Windows Admin Center in Azure Portal Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
Excel (3 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2025-26642 | Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-27750 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-27751 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Microsoft AutoUpdater for Mac (2 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2025-29800 | Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-29801 | Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Word (2 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2025-27747 | Microsoft Word Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2025-29816 | Microsoft Word Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Access (1 CVE)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2025-26642 | Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
ASP.NET (1 CVE)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2025-26682 | ASP.NET Core and Visual Studio Denial of Service Vulnerability |
Dynamics 365 (1 CVE)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2025-29821 | Microsoft Dynamics Business Central Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
OneNote (1 CVE)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2025-29822 | Microsoft OneNote Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Outlook for Android (1 CVE)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2025-29805 | Outlook for Android Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
Automation of Power (1 Common Vulnerability Exposure)
| Significant intensity | |
| CVE-2025-29817 | Information Disclosure Weakness in Microsoft Power Automate Desktop |
Structured Query Language Server (1 Common Vulnerability Exposure)
| Significant intensity | |
| CVE-2025-29803 | Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability in Visual Studio Tools for Applications and SQL Server Management Studio |
Centralized System (1 Common Vulnerability Exposure)
| Significant intensity | |
| CVE-2025-27743 | Elevation of Privilege Weakness in Microsoft System Center |
Visual Studio Tools for Applications (1 Common Vulnerability Exposure)
| Significant intensity | |
| CVE-2025-29803 | Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability in Visual Studio Tools for Applications and SQL Server Management Studio |
Appendix D: Notices and Different Products
There are 16 Adobe notices in this month’s release.
| CVE-2025-24446 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Input Verification |
| CVE-2025-24447 | APSB25-15 | Serialization of Untrusted Data |
| CVE-2025-30281 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Access Management |
| CVE-2025-30282 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Verification of Identity |
| CVE-2025-30283 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Input Verification |
| CVE-2025-30284 | APSB25-15 | Serialization of Untrusted Data |
| CVE-2025-30285 | APSB25-15 | Serialization of Untrusted Data |
| CVE-2025-30286 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Neutralization of Special Components used in an Operating System Instruction (‘OS Command Injection’) |
| CVE-2025-30287 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Verification of Identity |
| CVE-2025-30288 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Access Management |
| CVE-2025-30289 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Neutralization of Special Components used in an Operating System Instruction (‘OS Command Injection’) |
| CVE-2025-30290 | APSB25-15 | Incorrect Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory (‘Path Traversal’) |
| CVE-2025-30291 | APSB25-15 | Exposure of Information |
| CVE-2025-30292 | APSB25-15 | |
| CVE-2025-30293 | APSB25-15 | Inadequate Data Validation |
| CVE-2025-30294 | APSB25-15 | Inadequate Data Validation |
Appendix E: Affected Windows Server versions
This table lists the CVEs in the April release impacting nine Windows Server versions, from 2008 to 2025. The chart distinguishes between major iterations of the system without delving into specific details (e.g., Server Core). High-severity problems are highlighted in red, an “x” denotes the non-applicability of the CVE to that particular version. Admins are advised to utilize this appendix as a starting point to evaluate their individual risk, given that each reader’s scenario, particularly regarding products beyond standard support, will differ. For precise Knowledge Base references, it is recommended to refer to Microsoft. It should be noted that CVE-2025-27475 relates solely to a Windows client issue and is therefore included in this table minus any server versions marked.
| 2008 | 2008-R2 | 2012 | 2012-R2 | 2016 | 2019 | 2022 | 2022 23H2 | 2025 | |||||||
| CVE-2025-21174 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-21191 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-21197 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-21203 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-21204 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-21205 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-21222 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-24058 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-24060 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-24062 | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-24073 | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-24074 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26635 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26637 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability CVE-2025-26640 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | × | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability CVE-2025-26641 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability CVE-2025-26644 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | × | × | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability CVE-2025-26647 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability CVE-2025-26648 | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||
| CVE-2025-26649 | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26651 | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26652 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26663 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26664 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26665 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26666 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26667 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2025-26668 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| ■ | |||||||||||||||
| ■ | ■ | ||||||||||||||
| CVE-2025-26670 | × | ■ | |||||||||||||
| ■ | ■ | ||||||||||||||
| CVE-2025-26671 | × | ■ | |||||||||||||
| ■ | ■ | ||||||||||||||
| CVE-2025-26672 | ■ | ■ | |||||||||||||
| ■ | ■ | ||||||||||||||
| CVE-2025-26673 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability-2025-26674 | * | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||||
| Vulnerability-2025-26675 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||||||
| Vulnerability-2025-26676 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Vulnerability-2025-26678 | * | * | * | * | * | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26679 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26680 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26681 | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26686 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26687 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-26688 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27467 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | × | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27469 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27470 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ⬛ | ■ | × | ■ | |||||
| CVE-2025-27471 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||
| CVE-2025-27472 | × | × | ■ | ■ | × | × | × | × | |||||||
| CVE-2025-27473 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||
| CVE-2025-27474 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||
| CVE-2025-27475 | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27476 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | × | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27477 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||
| CVE-2025-27478 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||
| CVE-2025-27479 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27480 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27481 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27482 | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27483 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | × | × | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27484 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27485 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27486 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27487 | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27490 | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27491 | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27492 | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27727 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27728 | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27730 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | × | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27731 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||
| CVE-2025-27732 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||
| CVE-2025-27733 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2025-27735 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||
| CVE-2025-27736 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||
| CVE-2025-27737 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-27738 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| Exploit-2025-27740 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||||
| Exploit-2025-27741 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||||||
| Exploit-2025-27742 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | |||||||||||
| Exploit-2025-29808 | × | × | × | × | ■ | × | × | ||||||||
| CVE-2025-29809 | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-29810 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-29811 | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-29812 | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ||||||
| CVE-2025-29824 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |