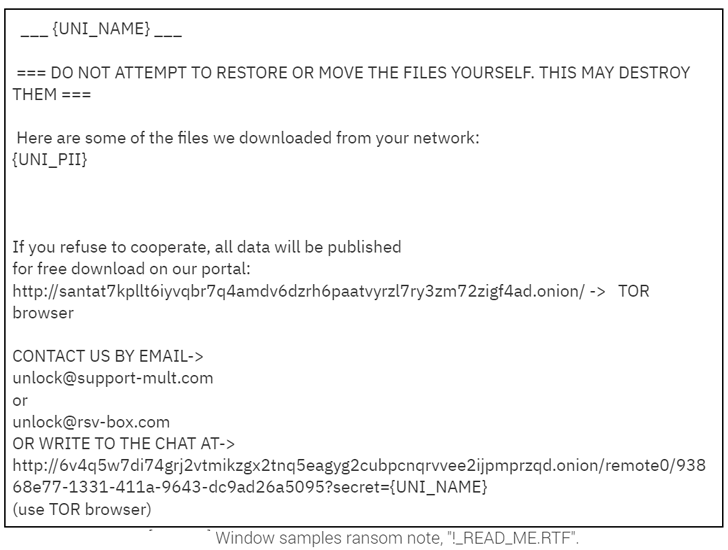
The
first-ever
Linux
variant
of
the
Clop
ransomware
has
been
detected
in
the
wild,
but
with
a
faulty
encryption
algorithm
that
has
made
it
possible
to
reverse
engineer
the
process.
“The
ELF
executable
contains
a
flawed
encryption
algorithm
making
it
possible
to
decrypt
locked
files
without
paying
the
ransom,”
SentinelOne
researcher
Antonis
Terefos
said
in
a
report
shared
with
The
Hacker
News.
The
cybersecurity
firm,
which
has
made
available
a
decryptor,
said
it
observed
the
ELF
version
on
December
26,
2022,
while
also
noting
its
similarities
to
the
Windows
flavor
when
it
comes
using
the
same
encryption
method.
The
detected
sample
is
said
to
be
part
of
a
larger
attack
targeting
educational
institutions
in
Colombia,
including
La
Salle
University,
around
the
same
time.
The
university
was
added
to
the
criminal
group’s
leak
site
in
early
January
2023,
per
FalconFeedsio.
Known
to
have
been
active
since
2019,
the
Clop
(stylized
as
Cl0p)
ransomware
operation
suffered
a
major
blow
in
June
2021
when
six
individuals
affiliated
with
the
gang
were
arrested
following
an
international
law
enforcement
operation
codenamed
Operation
Cyclone.
But
the
cybercrime
group
staged
an
“explosive
and
unexpected”
comeback
in
early
2022,
claiming
dozens
of
victims
spanning
industrial
and
tech
verticals.
SentinelOne
characterized
the
Linux
version
as
an
early-stage
version
owing
to
the
fact
that
some
functions
that
are
present
in
its
Windows
counterpart
are
missing.
This
lack
of
feature
parity
is
also
explained
by
the
fact
that
the
malware
authors
have
opted
to
build
a
custom
Linux
payload
rather
than
simply
porting
over
the
Windows
version,
suggesting
that
future
variants
of
Clop
could
close
those
gaps.
“A
reason
for
this
could
be
that
the
threat
actor
has
not
needed
to
dedicate
time
and
resources
to
improve
obfuscation
or
evasiveness
due
to
the
fact
that
it
is
currently
undetected
by
all
64
security
engines
on
VirusTotal,”
Terefos
explained.
The
Linux
version
is
designed
to
single
out
specific
folders
and
file
types
for
encryption,
with
the
ransomware
containing
a
hard-coded
master
key
that
can
be
utilized
to
recover
the
original
files
without
making
a
payment
to
the
threat
actors.
If
anything,
the
development
points
to
a
growing
trend
of
threat
actors
increasingly
venturing
beyond
Windows
to
target
other
platforms.
“While
the
Linux-flavored
variation
of
Cl0p
is,
at
this
time,
in
its
infancy,
its
development
and
the
almost
ubiquitous
use
of
Linux
in
servers
and
cloud
workloads
suggests
that
defenders
should
expect
to
see
more
Linux-targeted
ransomware
campaigns
going
forward,”
Terefos
said.
this
article
interesting?
Follow
us
on
and
to
read
more
exclusive
content
we
post.