A
new
Kaspersky
report
sheds
light
on
why
some
tech
pros
look
for
jobs
on
the
dark
web
and
how
to
spot
suspicious
and
likely
illegal
positions
from
recruiters
in
that
environment.

cendeced/Adobe
Stock
IT
professionals
are
actively
recruited
on
the
dark
web
with
job
ads
that
are
often
similar
to
legitimate
ones
from
regular
recruitment
websites.
According
to
Kaspersky’s
new
research,
this
tech
job
recruiting
environment
is
only
an
illusion
—
legal
jobs
are
rare
on
the
dark
web.
Jump
to:
Why
are
some
IT
pros
looking
for
jobs
on
the
dark
web?
The
number
of
ads
offered
on
the
dark
web
as
collected
by
Kaspersky
on
155
different
dark
web
forums
from
January
2020
to
June
2022
is
close
to
200,000,
with
peaks
during
the
COVID-19
pandemic
in
2020.
Some
reasons
that
might
prompt
someone
to
look
for
a
new
job
on
cybercriminals
forums,
even
when
considering
the
risks
of
being
caught
by
law
enforcement,
are:
-
Getting
laid
off. -
Pay
cuts. -
Lack
of
education
requirements. -
A
military
service
record. -
A
criminal
record
that
might
prevent
them
from
working
in
a
particular
area
of
expertise.
Sadly,
some
people
are
also
unaware
of
the
consequences
of
such
illegal
jobs
and
do
not
think
they
might
be
prosecuted.
How
recruiting
on
the
dark
web
usually
works
Employers
on
the
dark
web
market
rely
on
test
assignments
to
recruit
skilled
people.
Some
ads
are
more
specific
about
the
tests
and
allow
checking
the
required
level
(Figure
A);
people
are
often
paid
to
take
these
tests.
Figure
A

Kaspersky.
Translated
job
ad
selection
procedure.
Employers
also
do
interviews,
and
a
few
job
offers
mention
a
probationary
period.
One
unusual
requirement
is
that
only
people
without
addictions
will
be
selected.
To
attract
profiles,
dark
web
recruiters
mention
advantages
such
as
remote
working,
full-time
employment
or
flexible
schedules.
Yet
people
could
fall
prey
to
cybercriminal
organizations
such
as
FIN7,
whose
managers
do
not
hesitate
to
threaten
their
employees
who
did
not
appear
at
work
enough
or
thought
of
leaving
the
criminal
organization.
Most
recruited
tech
job
roles
on
the
dark
web
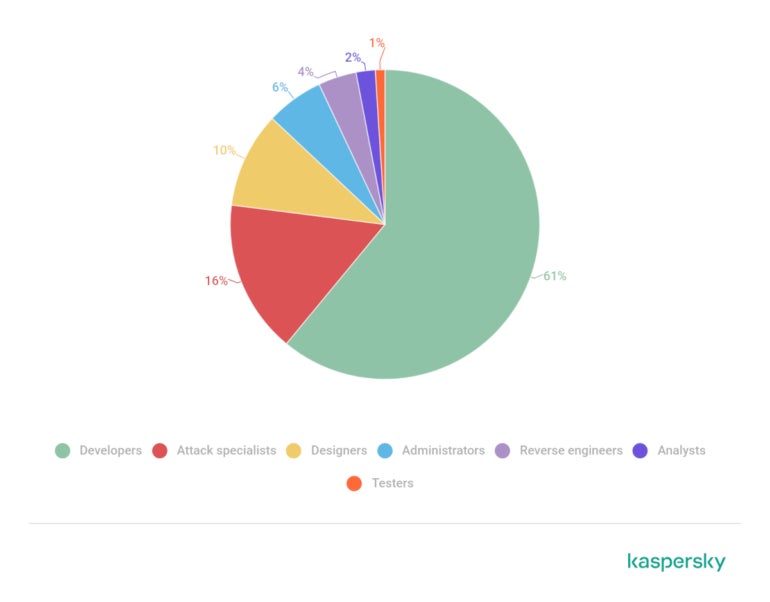
Developers
are
in
the
most
demand
in
this
environment,
followed
by
attack
specialists
(Figure
B).
Figure
B
Kaspersky.
Dark
web
jobs
are
advertised
across
specializations.
Threat
actors
are
especially
looking
for
these
tech
professionals:
-
Malware
developers,
since
most
attacks
use
malware
to
compromise
companies
or
exfiltrate
data
for
example. -
Penetration
testers
who
help
malware
developers
by
debugging
malware
and
helping
improve
anti-security
measures. -
Attack
specialists
who
are
able
to
perform
the
initial
intrusion
on
the
target
and
extend
it
inside
the
network. -
Reverse
engineers
for
reversing
tools,
creating
derived
ones
or
analyzing
code
that
needs
to
be
targeted. -
IT
administrators
to
configure
and
maintain
the
group’s
IT
infrastructure
and
make
sure
it
is
anonymized
and
running. -
Designers
who
create
fake
websites
and
phishing
emails. -
Analysts
who
gather
information
on
the
targeted
companies
and
provide
useful
information
to
help
launch
the
attack.
Median
salaries
for
these
jobs
on
the
dark
web
The
salaries
for
these
jobs
vary
depending
on
the
invested
effort
and
the
experience.
Salaries
are
often
paid
via
cryptocurrency.
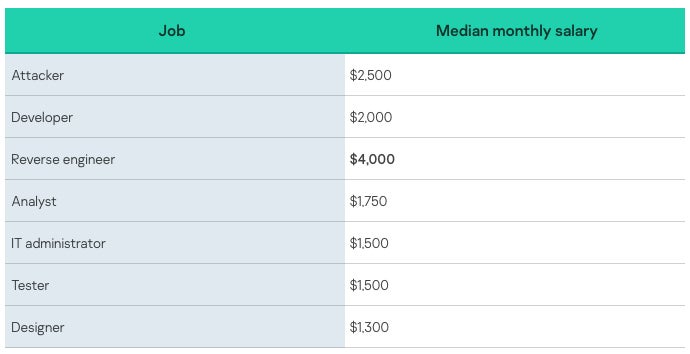
While
the
salary
range
varies
from
$200
to
$20,000
per
month,
median
salaries
show
that
it
is
rare
to
find
such
high
pay
(Figure
C).
Kaspersky’s
research
reveals
that
contrary
to
popular
belief,
cybercriminals’
jobs
are
not
paid
significantly
more
than
legitimate
jobs.
Figure
C
Kaspersky.
Median
monthly
salaries
across
specializations.
How
to
spot
a
suspicious
job
offer
from
the
dark
web
Some
jobs
ads
on
the
dark
web
do
look
similar
to
legitimate
postings,
so
users
should
always
be
careful
if
they
decide
to
follow
up
on
a
posting.
When
you’re
talking
to
the
recruiter,
it
will
likely
be
obvious
that
something
is
wrong
with
the
offer.
Here
are
red
flags
to
watch
with
such
job
offers.
-
A
real
employer
provides
a
full
identity
that
can
be
verified. -
A
real
employer
offers
a
real
contract
and
generally
does
not
pay
in
cryptocurrency. -
A
real
employer
can
provide
legal
documents
to
prove
the
existence
of
a
company,
depending
on
the
country
where
the
company
is
built,
which
seems
hard
to
provide
for
a
cybercriminal
threat
actor.
Read
next:
Mobile
device
security
policy
(TechRepublic
Premium)