Researchers
detailed
a
fully
undetectable
(FUD)
malware
obfuscation
engine
named BatCloak that
is
used
by
threat
actors.
Researchers
from
Trend
Micro
have
analyzed
the
BatCloak,
a
fully
undetectable
(FUD)
malware
obfuscation
engine
used
by
threat
actors
to
stealthily
deliver
their
malware
since
September
2022.
The
samples
analyzed
by
the
experts
demonstrated
a
remarkable
ability
to
persistently
evade
anti-malware
solutions.
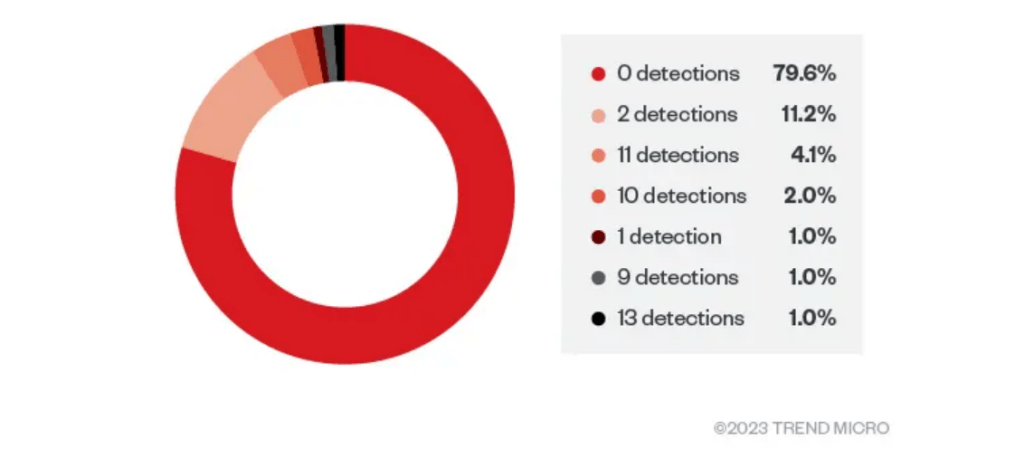
The
researchers
discovered
that
80%
of
the
retrieved
samples
had
zero
detections
from
security
solutions.
The
average
detection
rate
for
the
overall
sample
set
of
784
used
by
the
experts
was
less
than
one.
The
researchers
discovered
that
the
BatCloak
engine
was
part
of
FUD
builder
named
Jlaive
that
began
circulating
in
2022,
The
analysis
of
the
Jlaive
repository
revealed
the
developer
(ch2sh)’s
effort
in
FUD
technologies.
The
developers
used
AES
encryption
and
implemented
techniques
to
bypass
the
anti-malware
scan
interface
(AMSI).
After
the
repository
containing
the
open-source
tool
was
taken
down
in
September
2022,
it
has
since
been
cloned
and
modified
by
other
threat
actors.
The
researchers
discovered
modified
versions
and
clones
offered
Jlaive
as
a
one-time
service
for
purchase,
instead
of
a
classic
subscription-based
model.
While
many
of
the
repositories
containing
modified
or
cloned
Jlaive
versions
continue
to
be
removed
from
code
hosting
sites
such
as
GitHub
and
GitLab,
threat
actors
continue
to
upload
the
code
and
in
some
cases
development
team
have
also
ported
to
other
languages
such
as
Rust.

Jlaive
relies
on
a
modified
version
of
Nettitudes
RunPE
(runpe.dll),
an
open-source
C#
reflective
loader
for
unmanaged
binaries,
to
maintain
the
payload
in
memory
and
run
multiple
portable
executables
(PEs)
from
within
the
same
process
(process
hiving).
The
researchers
reported
that
the
BatCloak
engine
is
the
core
engine
of
Jlaive’s
obfuscation
algorithm
and
includes
LineObfuscation.cs
and
FileObfuscation.cs.
The
latter
algorithm
contains
the
logic
used
to
obfuscate
batch
files.
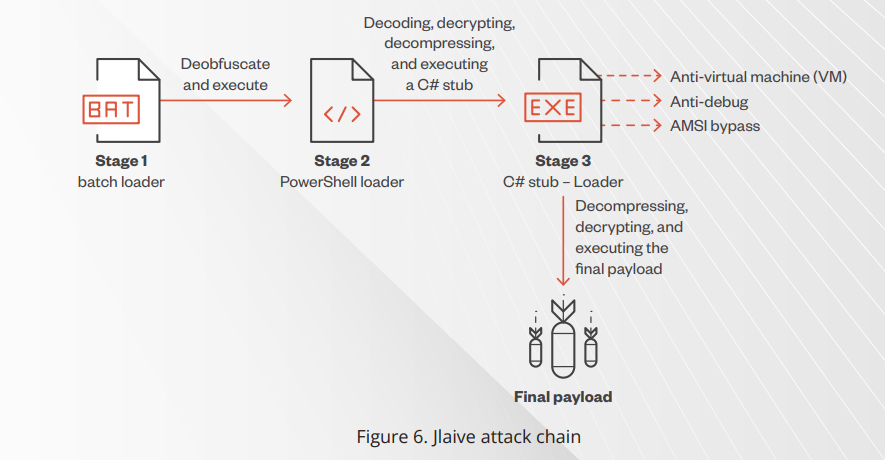
The
final
payload
is
packed
using
three
layers,
a
C#
loader,
a
PowerShell
loader,
and
a
batch
loader.
“The
last
step
for
the
builder
is
to
generate
a
batch
loader.
The
batch
loader
contains
an
obfuscated
PowerShell
loader
and
an
encrypted
C#
stub
binary.”
reads
the
analysis
published
by
Trend
Micro.
BatCloak
was
continuously
updated,
the
most
recent
version,
dubbed ScrubCrypt,
was
first
spotted
by
Fortinet
FortiGuard
Labs.
ScrubCrypt
is
designed
to
include
testing
on
a
host
of
popular
pieces
of
malware
such
as
Amadey,
AsyncRAT,
DarkCrystal
RAT,
Pure
Miner,
Quasar
RAT,
RedLine
Stealer,
Remcos
RAT,
SmokeLoader,
VenomRAT,
and
Warzone
RAT
(aka
Ave
Maria).
“The
evolution
of
BatCloak
underscores
the
flexibility
and
adaptability
of
this
engine
and
highlights
the
development
of
FUD
batch
obfuscators.”
concludes
the
report.
Follow
me
on
Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking,
BatCloak)