The most recent annual study from Sophos on the practical encounters with ransomware by healthcare enterprises delves into the entire victim journey, covering aspects from attack frequency and underlying cause to operational implications and business repercussions.
This year’s analysis brings to light new domains of investigation for the industry, such as examining ransom requests versus ransom disbursements and how frequently healthcare establishments seek assistance from law enforcement bodies to address the attack.
Access the report to discover the complete findings.
There has been an escalation in attack rates and recovery expenses
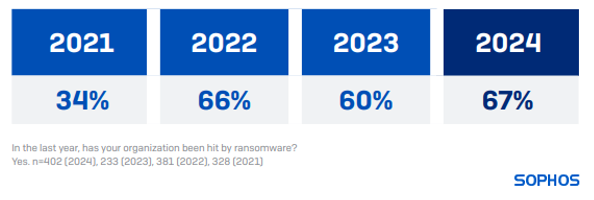
In 2024, 67% of healthcare organizations encountered ransomware attacks, an increase from the 60% documented in our 2023 research. The ransomware attack rate in healthcare this year is almost twofold compared to what was reported by the sector in 2021 (34%).
Within the last year, 95% of healthcare organizations affected by ransomware mentioned that cybercriminals tried to infiltrate their backups during the attack. Out of these attempts, two-thirds (66%) were successful. This marks one of the highest incidences of backup encroachments, with only the energy, oil/gas and utilities (79%) and education (71%) industries recording higher rates.
Out of ransomware attacks on healthcare entities, 74% resulted in data encryption, a figure nearly identical to the encryption rate from 2023 (73%). The sector observed a decline in solely extortion-based attacks, with only one respondent reporting such an incident, in contrast to 4% in our 2023 review.
The average expense for healthcare institutions to recover from a ransomware attack stood at $2.57M in 2024, an increase from the $2.20M documented in 2023.
Devices Affected in a Ransomware Incident
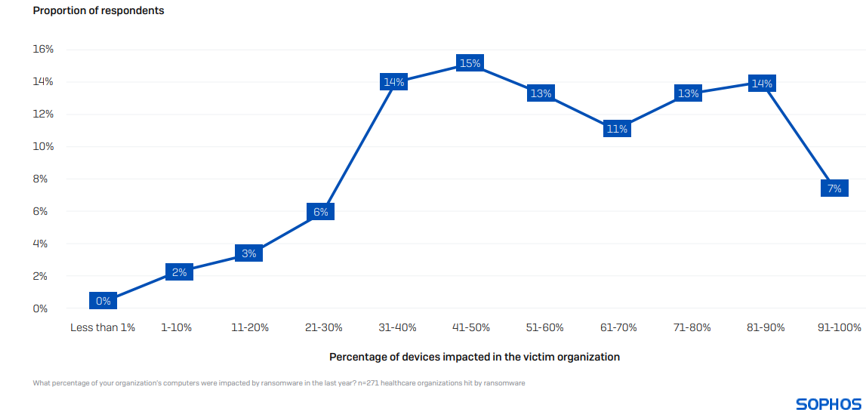
Typically, 58% of computers in healthcare organizations fall prey to a ransomware attack, exceeding the multi-sector norm of 49%. Instances where the entire environment is encrypted are exceedingly rare, with only 7% of institutions indicating that 91% or more of their devices were affected.
Tendency to Fulfill Ransom Demands is on the Rise
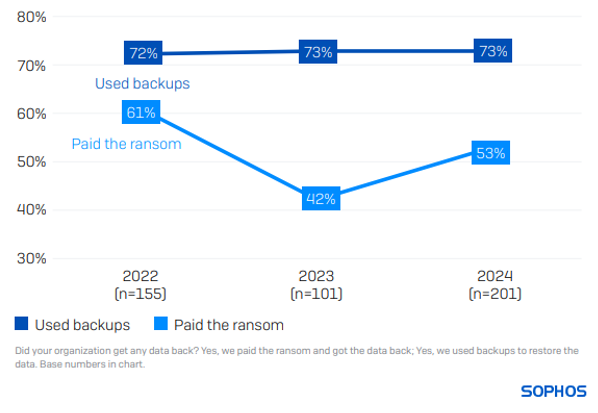
73% of healthcare establishments recovered encrypted data using backups, while 53% made ransom payments to retrieve their data. In contrast globally, 68% applied backups and 56% paid the ransom.
Over the past three years, the healthcare field’s use of backups has remained consistent (73% in 2023; 72% in 2022). However, the likelihood of healthcare organizations to pay ransom has notably increased over the previous year (42% in 2023), although it remains lower than the 61% reported in 2022.
A striking shift in the past year is the amplification in the inclination for victims to adopt multiple strategies to regain encrypted data (e.g., paying the ransom and employing backups). In this year’s examination, 52% of healthcare establishments that had data encrypted indicated using more than one approach, which is three times the rate recorded in 2023 (17%).
Rare Instances of Healthcare Victims Meeting the Initial Ransom Request
Among the 99 healthcare respondents whose organizations paid the ransom, they disclosed that the median amount paid was $1.5M in 2024.
Only 15% adhered to the initial ransom demand. 28% settled for less than the original demand, while 57% paid more. On average, across all healthcare respondents, organizations paid adversaries 111% of the initial ransom amount requested.
Download the complete report for further insights into ransom payments and various other aspects.
Survey Scope
The study is grounded on the outcomes of an unbiased, vendor-neutral survey arranged by Sophos involving 5,000 IT/cybersecurity leaders from 14 nations in the Americas, EMEA, and Asia Pacific, including 402 from the healthcare domain. All respondents represent firms with staff levels ranging from 100 to 5,000 members. The survey conducted by research specialist Vanson Bourne was carried out between January and February 2024, with participants providing insights based on their prior-year encounters.