Governance, risk, and compliance, commonly referred to as GRC, represent the methodologies and tools utilized to oversee an organization’s adherence to regulatory requirements and corporate governance standards.
The genesis of GRC dates back to 2003, with an in-depth examination presented by Scott L. Mitchell in a peer-reviewed paper published in 2007 within the International Journal of Disclosure and Governance. This article aims to elucidate the essence of GRC and its implications for both individuals and businesses.
Unraveling the Essence of GRC
GRC entails an organization’s encompassing approach towards navigating its interconnected elements. To gain insight into GRC, it’s beneficial to delve into each constituent aspect individually.
Sound Governance
Essentially, governance embodies the structure of rules, procedures, and methodologies that steer an organization’s direction and administration in meeting its objectives and business ambitions.
Risk Management
Referring to the likelihood of detriment or harm to an organization’s credibility, finances, workforce, clientele, or other stakeholders. central focus in GRC concerns risk management, i.e., pinpointing and subsequently mitigating risks encountered by the organization.
Adherence to Compliance
Signifies adherence to legislation, regulations, and standards prescribed by relevant entities or governmental bodies. Enforcement of compliance standards, contingent on the sector or industry, ensures that organizations adhere to a baseline operational standard.
Catalysts of GRC
Regulation unequivocally emerges as the predominant impetus behind GRC. Sectors such as healthcare, financial services, and tech enterprises endure the repercussions of regulatory actions. Amazon’s staggering GDPR fine of $877 million, disclosed in its 2021 Q2 financial report filed with the SEC, remains etched in our recent memory.
Most recently, Meta Platforms Ireland incurred a hefty €1.2 billion penalty in 2023 by the Irish Data Protection Authority for flouting data privacy laws through its renowned social media platform, Facebook. Meta’s violation encompassed the EU’s GDPR due to unauthorized data transfer from EU to US servers.
Corporate governance serves as another pivotal propeller of GRC. Investors exhibit an escalating interest in companies’ management practices and exposure to risks. Furthermore, stakeholders anticipate transparency in organizational operations and efficacious mechanisms to preempt misconduct.
Operational risks entwined with an organization’s day-to-day activities also impel GRC. These encompass perils linked to information security, supply chain oversight, and workforce welfare.
Significance of GRC
GRC is instrumental in shielding an organization’s image, finances, clientele, and workforce while ensuring alignment with pertinent legislation and regulations. Furthermore, GRC aids in refining operational efficacy and trimming costs.
By instituting a GRC regimen, organizations safeguard against hefty fines, penalties, and legal entanglements due to non-compliance. A well-executed GRC protocol facilitates the preemption of potential issues, thus saving time and resources in the long haul.
SEE: Securing Linux Policy (TechRepublic Premium)
Prominent GRC Tools
The burgeoning focus on GRC within the corporate domain has spurred the emergence of innovative GRC software, facilitating organizations of all scales in automating and streamlining their GRC methodologies. Here are a few exemplars:
Compliance Oversight Systems
These platforms aid in monitoring an organization’s compliance obligations by offering real-time insights into their compliance status. Additionally, they incorporate workflow functionalities, simplifying the management of compliance processes end-to-end.
Risk Mitigation Systems
These systems assist in identifying, evaluating, and mitigating operational risks. They commonly feature risk dashboards and heat maps to swiftly identify predominant risk areas.
Policy Implementation Platforms
These tools support in formulating, executing, and enforcing corporate policies and protocols. Typically, they include policy templates and workflows streamlining policy dissemination across the organization.
Unified platforms offering a comprehensive suite of GRC capabilities under one roof are favored by enterprises necessitating intricate GRC management.
For an in-depth exploration of GRC software tools and providers, delve into our Best GRC Tools compendium.
In this feature, we delve into the prime GRC tools catering to scalability, visibility, risk management, amongst other facets. Additionally, we expound on which business orientations can extract maximal benefits from implementing.GRC solutions.
Guidance for applying GRC in your enterprise
When it comes to executing a GRC initiative, there is no universal remedy. The optimal strategy will differ based on your organization’s size, intricacy, and requirements.
An effective method for implementing GRC can be found in the GRC Capability Model (Red Book) crafted by OCEG. This model comprises four elements: LEARN, ALIGN, PERFORM, and REVIEW.
Below we will delve into each fundamental component.
GRASP the correlation between GRC and your unique business demands
The primary phase is gaining a clear understanding of the laws, regulations, standards, culture, stakeholders, and the overall context relevant to your organization. It is also crucial to evaluate your organization’s risk tolerance and determine the types of risks you are prepared to handle. These assessments will shape your goals, strategies, and initiatives.
SYNC your approach with broader business targets
The subsequent step involves aligning your GRC approach with your enterprise’s goals and actions. This alignment ensures that your GRC initiative is in harmony with the overarching objectives of your organization.
EXECUTE measures and protocols to achieve favorable outcomes
The third stage necessitates taking measures that fortify the favorable aspects and counteract the undesirable ones. Additionally, it is important to have mechanisms in place to promptly identify deviations from GRC policies and procedures.
ASSESS and appraise GRC continuously
The final phase of this GRC model is to assess the design of your strategy, its operational efficiency, and the ongoing relevance of objectives to enhance your organization.
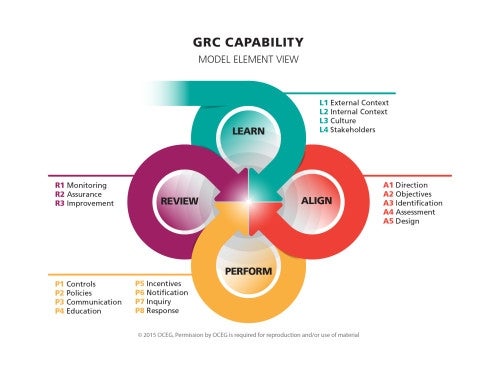
The GRC Capability Model furnishes a robust framework for contemplating and executing GRC within your operation. When wielded effectively, a GRC initiative can empower enterprises to adopt a proactive GRC standpoint — a critical factor in a company’s prosperity amidst today’s intricate commerce landscape.
This piece was initially published in September 2022. A revision was made by Luis Millares in January 2025.






