
With the deadline for EU Member States to implement the NIS 2 Directive nearing in October 2024, companies operating in Europe must get ready for the substantial alterations it introduces to cybersecurity adherence.
This piece aims to illuminate the NIS 2 Directive, its importance, significant changes from the original NIS Directive, and how enterprises can gear up for conformity. For a deeper exploration of the directive, access the Sophos NIS 2 Directive whitepaper.
What Does the NIS 2 Directive Entail?
The NIS 2 Directive represents a progression of the initial Network and Information Systems (NIS) Directive, devised to strengthen the cybersecurity framework of EU member states. The first NIS Directive, executed in 2016, set out guidelines to enhance cybersecurity resilience throughout the EU. However, with the surge in complexity and frequency of cyber assaults, notably during and post the Covid-19 outbreak, there emerged a clear necessity for stricter and more comprehensive regulations.
Cyber perils have heightened to an industrial scale, with ransomware attacks gaining particular prominence. In June 2024, a hacker group called Qilin, linked to the Kremlin, orchestrated an assault on Synnovis, a pathology lab utilized by the UK’s National Health Service. The hackers demanded £40 million as ransom, and when the NHS declined to pay, the hackers exposed the pilfered data on the dark web.
Furthermore, geopolitical tensions like the Russian incursion into Ukraine have underscored the urgency for robust cybersecurity measures. The intent of the NIS 2 Directive is to tackle these challenges by fortifying the security and resilience of crucial and significant entities across the EU.
Ramifications for Non-EU Businesses in the UK
While primarily targeting EU Member States, non-EU firms operating within the EU or catering to EU entities will also face repercussions. Numerous local regulations currently do not have as broad a reach as the NIS 2 Directive; nevertheless, it would be wise to anticipate further modifications to local laws as the EU legislation plans progress.
By proactively tackling the challenges outlined below, non-EU enterprises can enhance their safeguarding against evolving cyber risks, while steering clear of hefty penalties for non-compliance.
Noteworthy Changes from NIS to NIS 2
The NIS 2 Directive introduces several crucial updates and extensions from the original NIS Directive:
- Expanded Coverage of Included Entities:
- Vital and Crucial Entities: NIS 2 segregates entities into “essential” and “important” categories depending on their sector and criticality. This enlargement encompasses more sectors like wastewater, healthcare supply chains, postal and courier services, aerospace, public administration, and digital infrastructure.
- Supply Chain and Service Providers: Institutions implicated in the supply chain and those dispensing essential support services are now explicitly covered, emphasizing the significance of securing interlinked networks.
- Augmented Cybersecurity Standards:
- Obligatory Measures: Article 21 of the directive lays down compulsory cybersecurity measures, encompassing fundamental cyber hygiene, vulnerability management, supply chain security, encryption, asset management, access control, and zero trust security.
- Incident Handling and Reporting: The directive mandates stricter incident reporting requirements, assuring prompt and consistent responses to cyber threats throughout the EU.
- Intensified Accountability and Penalties:
- Senior Management Responsibility: Senior management can face personal liability for non-compliance, emphasizing the necessity of executive participation in cybersecurity governance.
- Monetary Penalties and Sanctions: Entities could encounter substantial fines, up to €10 million or 2% of global turnover, for failing to conform with the directive.
The subsequent 18 sectors fall under the purview of the NIS 2 Directive:
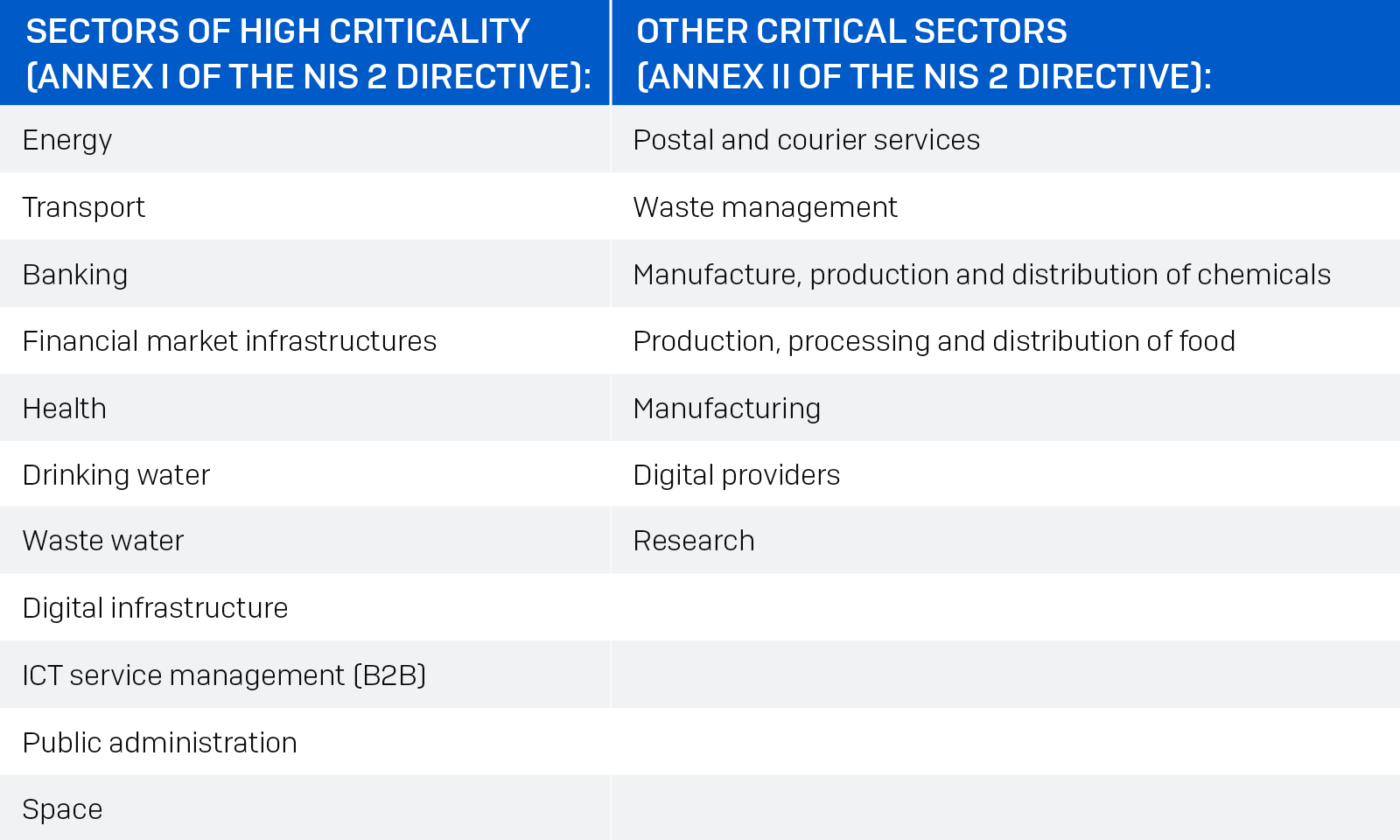
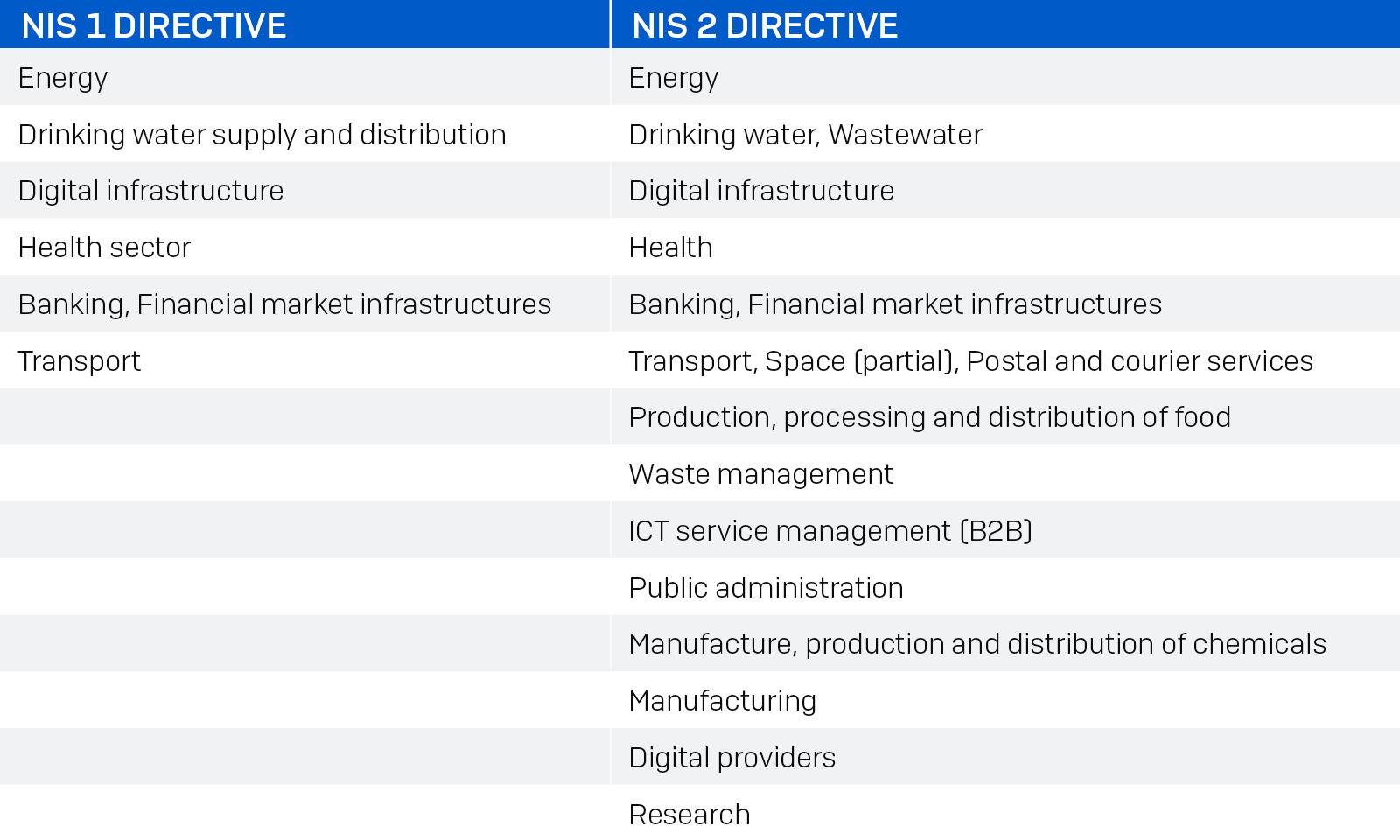
The following table demonstrates the broadening spectrum of sectors under the NIS 2 Directive vis-à-vis the initial NIS directive:
Effect on Cybersecurity Adherence
The NIS 2 Directive significantly transforms how enterprises tackle cybersecurity conformity. Firms must embrace a proactive approach, amalgamating comprehensive risk management protocols and ensuring adherence to the stringent benchmarks delineated in the directive. The emphasis on mandatory measures and the potential for severe penalties necessitate a thorough reassessment and enhancement of prevailing cybersecurity methodologies.
Enterprises will need to assign adequate resources to meet these requisites. Estimations indicate that companies previously encompassed by the original NIS Directive may need to elevate their cybersecurity budgets by up to 12%, while those freshly covered could witness budget increments of up to 22%, as stated by John Noble, ex-Director of the National Cyber Security Centre in a discourse on Sophos Spotlight: NIS2 Directive and Understanding Cybersecurity Compliance.
Preparation for NIS 2 Conformity
To assure compliance with the NIS 2 Directive, companies should undertake the subsequent actions:
- Evaluate Applicability:
- Ascertain whether your enterprise corresponds to the essential or important entities’ categories. This involves evaluating your sector, the criticality of your services, and your operational presence within the EU.
- Comprehend Jurisdiction:
- Recognize which EU member states hold jurisdiction over your functions for NIS 2 purposes. This is pivotal for understanding specific national requisites and reporting obligations.
- Enforce Cybersecurity Risk Management:
- Undertake a comprehensive risk assessment to pinpoint potential cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
- Execute the mandatory measures expounded in Article 21, aligning them with an apt security framework such as ISO 27001 or the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
- Bolster Supply Chain Security:
- Prioritize mitigating risks within your supply chain, particularly concerning software and service providers. This entails ensuring that third-party vendors adhere to NIS 2 standards.
- Create an Incident Response Strategy:
- Formalize an incident response strategy that encompasses explicit protocols for reporting cyber incidents to pertinent national authorities. Ensure that significant incidents are reported within the specified 24-hour duration by the directive.
- Engage Senior Management:
- Secure formal endorsement from top-tier management for your compliance approach. Senior management engagement is pivotal for showcasing a dedication to cybersecurity and guaranteeing the allocation of requisite resources.
The NIS2 Directive marks a significant leap forward in bolstering the cybersecurity resilience of enterprises across Europe. By assimilating the key updates and taking proactive measures to ensure conformity, companies can fortify themselves against the escalating menace of cyber-attacks.
With the October cutoff approaching, it is imperative for top management and IT security professionals to prioritize NIS 2 conformity, leveraging resources like the Sophos whitepaper to pilot their endeavors.



