Cyber Liability Insurance and Cyber Security Measures 2024: Insights from IT and Cybersecurity Experts


Cyber jeopardy is inescapable. In today’s corporate landscape, the objective should not center on eradicating risk, but rather managing it as effectively as feasible. Two primary methods are handling through implementing cyber safeguards and tweaking user behaviors, and allocation through cyber coverage. These methods are interlinked: robust safeguards lower risk which enhances accessibility to coverage, while feeble safeguards elevate risk, complicating the acquisition of cost-effective policies.
Today we have unveiled an innovative analysis that delves deep into this correlation. Based on an impartial poll of 5,000 IT decision-makers, it scrutinizes cyber insurance incorporation among mid-level organizations, showcasing buying catalysts, the consequence of defense investments on insurability, and explanations why cyber incidents costs sometimes remain partially uncovered.
Synopsis for Executives
Amidst inevitable cyber assaults, embracing an all-encompassing strategy towards cyber risk management that exploits the interaction between cyber security measures and cyber insurance will empower entities to downscale their overall total cost of ownership (TCO) of cyber risk management while diminishing their likelihood of encountering a major breach.
The research also discloses that funneling resources into cyber defenses not only simplifies and reduces the cost of obtaining insurance but also enhances protection and cuts down on IT workload. This discovery underscores the significance of contemplating cyber risk investments holistically, rather than in isolation.
One area of apprehension underscored by the poll is the potential of policy acquisitions to be misaligned with business requisites. Cyber insurance stands as an investment, hence policies must encompass pertinent risks. All stakeholders, especially IT and cybersecurity units, need to be engaged in selecting policies to ensure alignment with the entity’s requirements.
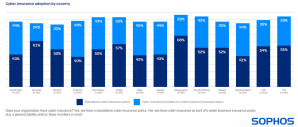
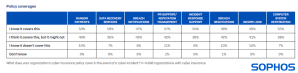
Incorporation of cyber insurance is prevalent
The poll validates that integration of cyber insurance is prevalent among entities spanning 100-5,000 employees, with 90% of entities harboring some form of cyber protection. Half possess a standalone policy while 40% have cyber insurance as part of a broader business insurance policy, such as a comprehensive liability policy. Incorporation levels are elevated across all 14 nations that underwent the survey, with Singapore registering the highest inclination to possess coverage.
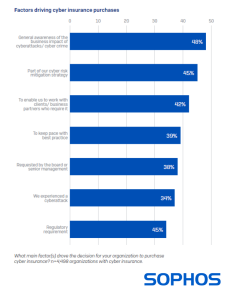
Cognizance of the business consequences of cyberattacks is the most commonplace stimulant behind insurance take-up
Entities embrace cyber insurance for myriad and diverse reasons, with about half (48%) attributing knowledge of the business repercussions of cyberattacks as the chief motivator. 45% indicated it was a part of their cyber risk mitigation stratagem and 42% mentioned that they require cyber insurance to engage with clients or partners who mandate it.
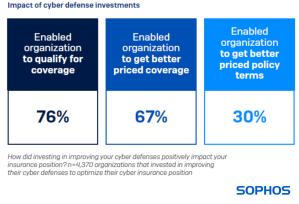
Channeling resources into cyber defenses to fine-tune insurance standing is a conventional practice – and it’s yielding results
97% of entities that procured cyber insurance last year elevated their defenses to fine-tune their insurance standing. Almost two-thirds (63%) made substantial allocations, while 34% made minor ones.
These security investments are bearing fruit, as the poll found that nearly every entity that channeled resources into improving their cyber defenses conveyed that it had a beneficial impact on their cyber insurance standing (99.6%, 4,351 out of 4,370 respondents).
Cyber insurance requisites are compelling entities to bolster their defenses (the “stick”), with 76% of respondents affirming that their investments secured coverage they previously couldn’t access. The “carrot” being that about two-thirds (67%) managed to secure better-priced coverage, and 30% gained improved terms owing to their enhanced protection (e.g., widened coverage limits).
Additionally, entities investing in security reaped benefits extending beyond insurance. 99% reported broader gains such as enhanced protection, diminished alerts, and reduced IT burden.
Insurers almost invariably disburse in some form on a claim
Entities that have invested in a cyber policy will be relieved to know that insurers nearly always compensate in some form on a claim, with just one respondent stating their claim was entirely repudiated.
On the flip side, in 99% of claims, insurers didn’t cover the entire incident cost. In a holistic view, insurers typically defrayed 63% of the total incident cost, with the most recurrent payout rate hovering between 71-80%.
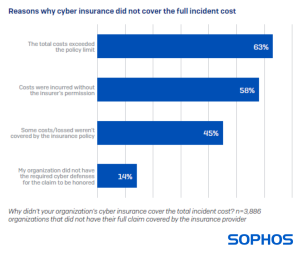
Causes for expenditures
insufficient coverage
It was disclosed by the survey that the expenses incurred in recovering from cyberattacks are surpassing the protection provided by insurance policies. The primary reason (63%) for not being fully compensated for the recovery expenses was that the total costs exceeded the limits of the policy. As per the 2024 survey on Ransomware by Sophos, the costs of recovery following a ransomware incident have surged by 50% in the past year, causing a likely discrepancy between policies and costs.
There is substantial uncertainty regarding the scope of coverage in case of a cyber incident
A large number of cybersecurity/IT leaders are uncertain about the scope of their policy in the event of an incident. Among those possessing a policy, 40% believe it includes ransom payments, and 41% believe it includes loss of income, although they are not entirely sure. These results raise concerns on multiple levels:
- Organizations are at risk of receiving inadequate coverage – highlighted by 45% of those whose expenses from incidents were not entirely covered stating that some costs/losses were not included in their insurance policy
- Organizations may not receive the expected support in the event of filing a claim
The lack of clarity on policy coverage likely stems, at least partially, from a disparity between those procuring the policy and those dealing with a major incident on the ground.
Explore the complete report
For more thorough insights, including an examination of the influence of cyber insurance coverage on ransomware outcomes and various other aspects, access the full report.
Regarding the survey
The report is based on the results of an independent, neutral survey commissioned by Sophos among 5,000 IT/cybersecurity leaders in 14 countries across the Americas, EMEA, and Asia Pacific. All participants represent companies with staff counts ranging from 100 to 5,000 employees. The survey was conducted by research expert Vanson Bourne between January and February 2024, and respondents were asked to provide insights based on their experiences over the preceding year.