August 2024 witnessed an extensive release for Patch Tuesday by Microsoft. Unlike the previous month with a flood of 138 Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) to address, this time around the main release tackled just around 85 CVEs. However, alongside more than twenty advisories, including informational notices spanning materials disclosed in June and July, coupled with two high-profile issues still in the progress of receiving fixes, and over 85 Linux-related CVEs being covered in this release, administrators may find the prioritization of patches particularly intricate this month.
During the patch application phase, it was identified that five of the issues that were resolved were already being exploited in the wild. Furthermore, an additional three issues had been publicly disclosed. Microsoft’s assessment indicated that 11 CVEs, all within the Windows system, were more susceptible to exploitation in the upcoming 30 days based on the company’s analysis. Out of this month’s problematic occurrences, nine are capable of being detected by Sophos protections, with detailed information provided on these in the table below.
Aside from the patches released, there was an inclusion of detailed advisory information on 12 Adobe patches, nine for Edge via Chrome (in addition to three Edge patches from Microsoft), and the usual servicing stack update (ADV990001). Notably, five previously unannounced CVEs that were addressed earlier during the summer (one in June and four in July) were highlighted. These CVEs have been listed in Appendix D below, with a reminder for those who have already applied fixes during those respective months, ensuring they are already safeguarded and don’t require reapplication. It is essential to highlight an issue patched in June, specifically CVE-2024-38213, which is currently under active exploitation in the wild, further justifying the urgency to apply patches promptly after release. Microsoft also took a step to flag three other CVEs for which fixes had already been deployed but were included in the Patch Tuesday information for the sake of transparency, with these listed in Appendix D as well. Lastly, appendices presenting Microsoft’s patches are included, sorted by severity, predicted exploitability, and product categorization.
This month’s release also encompassed a substantial number of CVEs related to CBL-Mariner, or in some instances, linked to both Mariner and Azure Linux. Although Mariner underwent a renaming to Azure Linux earlier in the year, the details provided by Microsoft regarding these CVEs distinguished between the two. Ranging from a timespan of 2007 to 2024, the CVSS base scores varied from 3.2 to a top tier “perfect” 10. These specific CVEs are excluded from the primary data presented in this post, but they have been consolidated in Appendix E towards the end of this publication for reference. Additionally, two extra Mariner/Azure Linux CVEs interconnect with Windows, and these two have been included in the statistical data in the primary article as well as enumerated in the list found in Appendix E.
The provided data in the main content pertains solely to the 85 CVEs in the release that do not relate to Mariner or the advisory section.
Statistical Overview
- Total CVEs: 85
- Total Edge/Chrome advisory issues covered in the update: 9 (in addition to 3 non-advisory Edge matters)
- Total non-Edge Microsoft advisory issues covered in the update: 9
- Total Adobe issues covered in the update: 12
- Publicly disclosed: 3
- Currently exploited: 5
- Severity
- Critical: 6
- Important: 77
- Moderate: 2
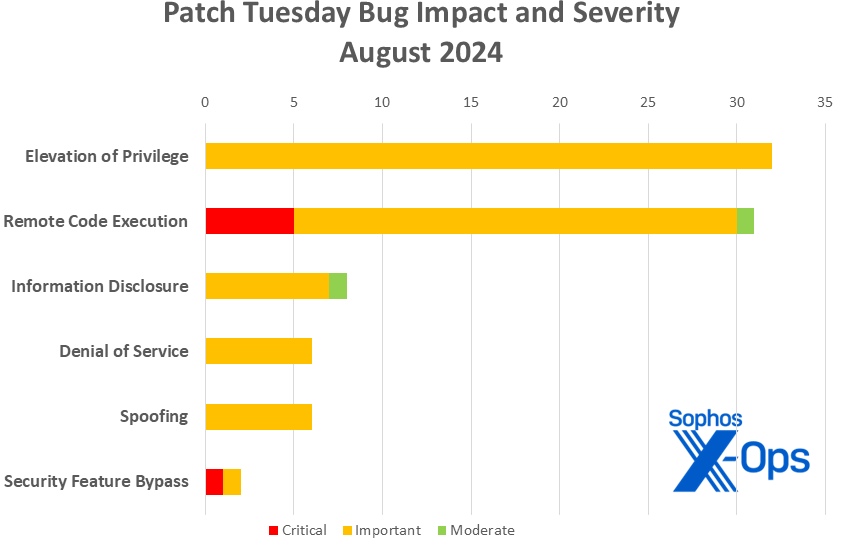
- Impact
- Elevation of Privilege: 32
- Remote Code Execution: 31
- Information Disclosure: 8
- Denial of Service: 6
- Spoofing: 6
- Security Feature Bypass: 2
Figure 1: The six critical-severity vulnerabilities addressed in August’s Patch Tuesday release include the second this year involving security feature bypass. (This chart does not represent the Mariner-related issues discussed elsewhere in this article)
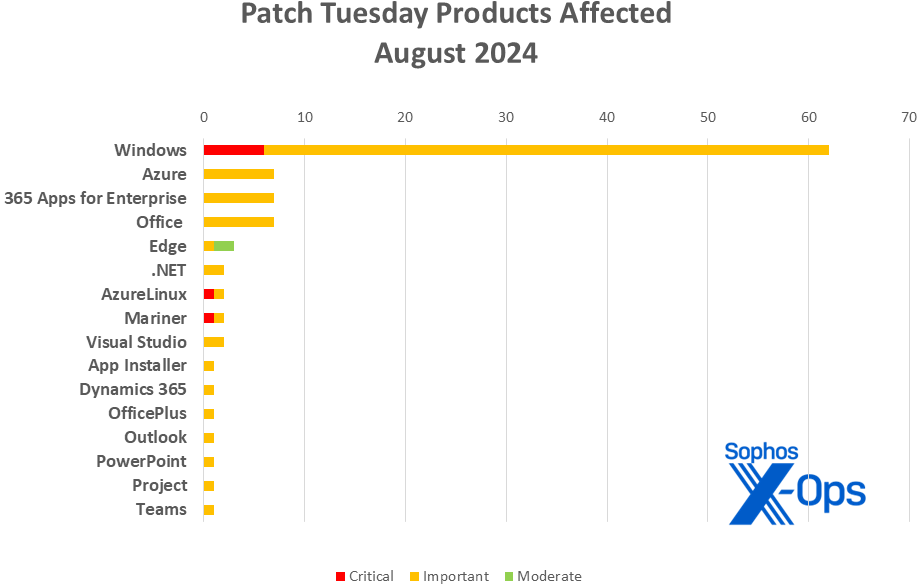
Product Breakdown
- Windows: 62
- Azure: 7
- 365 Apps for Enterprise: 7
- Office: 7
- Edge: 3 (along with 9 advisories via Chrome)
- .NET: 2
- Azure Linux: 2
- CBL-Mariner: 2
- Visual Studio: 2
- App Installer: 1
- Dynamics 365: 1
- OfficePlus: 1
- Outlook: 1
- PowerPoint: 1
- Project: 1
- Teams: 1
Consistent with the convention for cataloging this list, CVEs that impact multiple product families have been tabulated accordingly per the relevant family.
Figure 2: A diverse range of product families are impacted by the patches in August’s release; highlighting the intriguing obscurity of at least one, App Installer, prompting Microsoft to include a link for further details in the release, with information on updating via winget. Windows, however, retains its dominant presence
Highlighted August Updates
Beyond the aforementioned concerns, a lineup of specific elements warrants special mention.
CVE-2024-21302 – Windows Secure Kernel Mode Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38202 – Windows Update Stack Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Recently brought to light by researcher Alon Leviev at Black Hat, these two significant-severity issues were unveiled following an extended responsible disclosure process. Microsoft has been diligently working on the resolution for six months; however, a bit more time is required to tackle the intricate nature of the issue concerning Virtualization-Based Security (VBS). In the interim, Microsoft has released mitigation details for both CVE-2024-21302 and CVE-2024-38202 on their official site.
CVE-2024-38063 – Windows TCP/IP Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Among the trio of CVEs boasting a 9.8 CVSS base score in this release, this specific one stands out as Microsoft identifies it as more inclined to be exploited within the next thirty days. Regrettably, this critical-severity Remote Code Execution (RCE) flaw requires no privileges or user interaction for exploitation. An assailant could potentially leverage this vulnerability by maliciously sending IPv6 packets, interspersed with specially crafted IPv6 packets, to a Windows system equipped with IPv6 functionality. (Systems with IPv6 disabled would remain unaffected by such an attack.) Sophos has promptly issued shields (Exp/2438063-A) for this matter, highlighted in the subsequent table.
CVE-2024-38213
Security Vulnerability Bypass with Windows Mark of the Web
This particular concern is among the five indicated earlier that had actually been resolved several months back (specifically in June 2024). Individuals who have implemented the updates that were issued in June are safeguarded; those who have not done so are encouraged to apply the updates promptly, as there are ongoing malicious activities targeting this vulnerability.
[42 CVEs] Windows 11 Updates for 24H2, Already Available
While Windows 11 24H2 has not yet been officially released, nearly half of the issues addressed this month pertain to that specific operating system. Users of the new Copilot+ PCs who do not receive updates automatically need to ensure they update their devices promptly; conversely, those who do receive automatic updates should have already acquired all required patches through the most recent comprehensive update, which raises the device versions to Build 26100.1457.
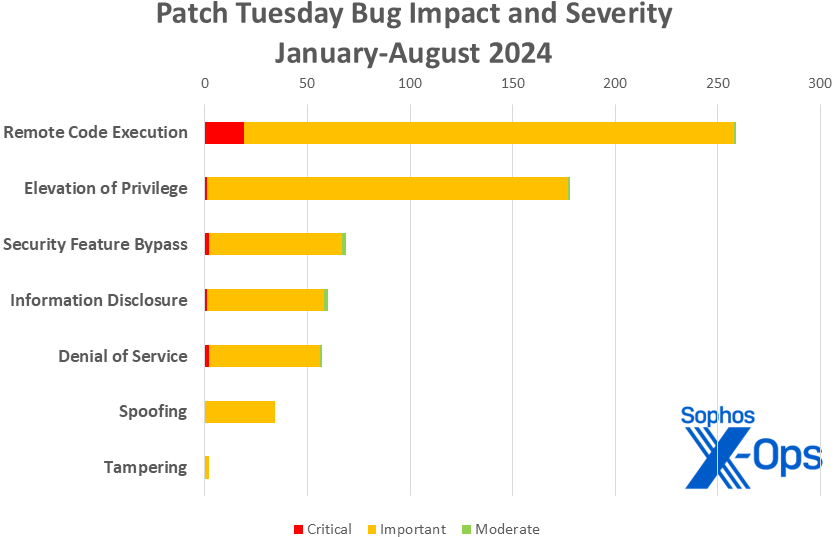
Figure 3: With a total of 659 CVEs addressed in Patch Tuesday releases thus far in 2024, Microsoft is handling a significantly higher workload compared to the same period in 2023 (491 patches), although slightly lower than the workload in 2022 (690 patches). It is important to note that this data does not encompass the 84 Mariner-released CVEs discussed elsewhere in this post.
Sophos Security Measures
| CVE | Sophos Intercept X/Endpoint IPS | Sophos XGS Firewall |
| CVE-2024-38063 | Exp/2438063-A | |
| CVE-2024-38106 | Exp/2438106-A | |
| CVE-2024-38141 | Exp/2438141-A | |
| CVE-2024-38144 | Exp/2438144-A | |
| CVE-2024-38147 | Exp/2438147-A | |
| CVE-2024-38150 | Exp/2438150-A | |
| CVE-2024-38178 | 2309977 | |
| CVE-2024-38193 | Exp/2438193-A | |
| CVE-2024-38196 | Exp/2438196-A |
Just like every month, if you are not keen on waiting for your system to automatically retrieve Microsoft’s updates, you have the option to manually download them from the Windows Update Catalog website. Use the winver.exe tool to identify the Windows 10 or 11 build you are using, and then download the Cumulative Update package suitable for your system’s architecture and build version.
Appendix A: Severity and Impact of Vulnerabilities
This categorization presents August patches organized by impact, further categorized by severity levels, and subsequently sorted by CVE.
Privilege Elevation (32 CVEs)
| Significance: Important | |
| CVE-2024-21302 | Windows Secure Kernel Mode Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-29995 | Windows Kerberos Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38084 | Microsoft OfficePlus Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
Appendix B: Vulnerability
Here is a compilation of the August CVEs categorized by Microsoft as either actively exploited or more susceptible to exploitation within the initial 30 days post-release. The information is sorted by CVE. Note that CVE-2024-38213, launched in June, is not listed.
| Exploited vulnerability identified | |
| CVE-2024-38106 | Windows Kernel Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38107 | Windows Power Dependency Coordinator Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38178 | Scripting Engine Memory Exploitation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38189 | Microsoft Project Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38193 | Windows WinSock Ancillary Function Driver Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| More probable exploitation in the next 30 days | |
| CVE-2024-38063 | Windows TCP/IP Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38125 | Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38133 | Windows Kernel Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38141 | Windows WinSock Ancillary Function Driver Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38144 | Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38147 | Microsoft DWM Core Library Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38148 | Windows Secure Channel Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38150 | Windows DWM Core Library Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38163 | Windows Update Stack Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38196 | Windows Common Log File System Driver Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38198 | Windows Print Spooler Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
Appendix C: Affected Products
Below, you will find the August patches grouped by product family, then arranged by severity. Each list is further categorized by CVE. Patches applicable to multiple product families are included in each respective family’s list.
Windows (62 CVEs)
| Severe severity | |
| CVE-2022-3775 | Redhat: CVE-2022-3775 grub2 – Vulnerability in rendering specific Unicode sequences can result in heap-based out-of-bounds write |
| CVE-2023-40547 | Redhat: CVE-2023-40547 Shim – Remote code execution in HTTP boot support could result in bypassing secure boot |
| CVE-2024-38063 | Windows TCP/IP Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38140 | Windows Reliable Multicast Transport Driver (RMCAST) Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38159 | Windows Network Virtualization Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38160 | Windows Network Virtualization Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Significant severity | |
| CVE-2022-2601 | Redhat: CVE-2022-2601 grub2 – Buffer overflow in grub_font_construct_glyph() may cause out-of-bound write and possible secure boot bypass |
| CVE-2024-21302 | Windows Secure Kernel Mode Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-29995 | Windows Kerberos Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-37968 | Windows DNS Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38106 | Windows Kernel Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38107 | Windows Power Dependency Coordinator Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38114 | Windows IP Routing Management Snapin Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38115 | Windows IP Routing Management Snapin Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38116 | Windows IP Routing Management Snapin Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38117 | Windows Named Pipe Filesystem Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38118 | Microsoft Local Security Authority (LSA) Server Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38120 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38121 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38122 | Microsoft Local Security Authority (LSA) Server Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38123 | Windows Bluetooth Driver Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38125 | Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38126 | Windows Network Address Translation (NAT) Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38127 | Windows Hyper-V Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38128 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38130 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38131 | Clipboard Virtual Channel Extension Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38132 | Windows Network Address Translation (NAT) Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38133 | Windows Kernel Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38134 | Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver Privilege Elevation Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38135 | |
| CVE-2024-38136 | Windows Resource Manager PSM Service Expansion Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38137 | Windows Resource Manager PSM Service Expansion Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38138 | Windows Deployment Services Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38141 | Windows Auxiliary Feature Driver for WinSock Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38142 | Windows Secure Core Mode Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38143 | Windows WLAN AutoConfig Service Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38144 | Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38145 | Windows Layer-2 Bridge Network Driver Denial of Service Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38146 | Windows Layer-2 Bridge Network Driver Denial of Service Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38147 | Microsoft DWM Core Library Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38148 | Windows Secure Channel Denial of Service Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38150 | Windows DWM Core Library Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38151 | Windows Kernel Information Leakage Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38152 | Windows OLE Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38153 | Windows Kernel Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38154 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38155 | Security Center Broker Information Leakage Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38161 | Windows Mobile Broadband Driver Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38163 | Windows Update Stack Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38178 | Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38180 | SmartScreen Prompt Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38184 | Windows Kernel-Mode Driver Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38191 | Kernel Streaming Service Driver Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38193 | Windows Auxiliary Feature Driver for WinSock Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38196 | Windows Common Log File System Driver Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38198 | Windows Print Spooler Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38199 | Windows Line Printer Daemon (LPD) Service Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38202 | Windows Update Stack Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38214 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Information Leakage Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38215 | Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38223 | Windows Initial Machine Configuration Privilege Escalation Weakness |
Azure (7 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2024-38098 | Azure Connected Machine Agent Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38108 | Azure Stack Spoofing Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38157 | Azure IoT SDK Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38158 | Azure IoT SDK Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38162 | Azure Connected Machine Agent Privilege Escalation Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38195 | Azure CycleCloud Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38201 | Azure Stack Hub Privilege Escalation Weakness |
365 Apps for Enterprise (7 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2024-38169 | Microsoft Office Visio Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38170 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38171 | Microsoft PowerPoint Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38172 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38173 | Microsoft Outlook Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38189 | Microsoft Project Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38200 | Microsoft Office Spoofing Weakness |
Office (7 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2024-38169 | Microsoft Office Visio Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38170 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38171 | Microsoft PowerPoint Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38172 | Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38173 | Microsoft Outlook Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38189 | Microsoft Project Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38200 | Microsoft Office Spoofing Weakness |
Edge (3 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2024-38218 | Microsoft Edge (HTML-based) Memory Corruption Weakness |
| Moderate severity | |
| CVE-2024-38219 | Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Remote Code Execution Weakness |
| CVE-2024-38222 | Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) Information Disclosure Weakness |
.NET (2 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38167 | .NET and Visual Studio Exposure of Information Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38168 | .NET and Visual Studio Service Denial Weakness |
Azure Linux (2 CVE)
| Vital severity | |
| CVE-2022-3775 | Redhat: Bug in grub2 with CVE-2022-3775 – Writing data out-of-bounds when displaying certain Unicode sequences |
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2022-2601 | Redhat: Vulnerability in grub2 with CVE-2022-2601 – Writing beyond the allocated memory in grub_font_construct_glyph() and the potential to bypass secure boot |
CBL-Mariner (2 CVE)
| Vital severity | |
| CVE-2022-3775 | Redhat: Security flaw in grub2 identified by CVE-2022-3775 – Writing data out-of-bounds when rendering certain Unicode sequences |
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2022-2601 | Redhat: Weakness in grub2 with CVE-2022-2601 – Writing beyond allocated memory in grub_font_construct_glyph() leading to potential secure boot bypass |
Visual Studio (2 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38167 | .NET and Visual Studio Exposure of Information Vulnerability |
| CVE-2024-38168 | .NET and Visual Studio Service Denial Weakness |
App Installer (1 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38177 | Security vulnerability in Windows App Installer allowing Spoofing |
Dynamics 365 (1 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38211 | Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in Microsoft Dynamics 365 (on-premises) |
OfficePlus (1 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38084 | Microsoft OfficePlus Privilege Escalation Weakness |
Outlook (1 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38173 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Outlook |
PowerPoint (1 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38171 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft PowerPoint |
Project (1 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38189 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Project |
Teams (1 CVE)
| Urgent severity | |
| CVE-2024-38197 | Spoofing Vulnerability in Microsoft Teams for iOS |
Appendix D: Alerts and Other Applications
Here’s a compilation of alerts and details on other significant CVEs in the August Microsoft release, organized by product.
Pertinent to Edge / Chromium (9 CVEs)
| CVE-2024-6990 | Chromium: Uninitialized Usage in Dawn identified with CVE-2024-6990 |
| CVE-2024-7255 | Out-of-bounds Read identified in WebTransport as CVE-2024-7255 |
| CVE-2024-7256 | Data Validation Shortcoming in Dawn with CVE-2024-7256 |
| CVE-2024-7532 | Memory Access Out of Bounds in ANGLE tracked with CVE-2024-7532 |
| CVE-2024-7533 | Free Usage after Allocation in Sharing reported as CVE-2024-7533 |
| CVE-2024-7534 | Buffer Overflow in Layout leading to Heap Corruption as CVE-2024-7534 |
| CVE-2024-7535 | Inadequate Implementation in V8 noted under CVE-2024-7535 |
| CVE-2024-7536 | Free Usage after Allocation in WebAudio as identified in CVE-2024-7536 |
| CVE-2024-7550 | Confusion of Types in V8 leading to Type Confusion under CVE-2024-7550 |
Servicing Stack Updates (1 item)
| ADV990001 | Most Recent Servicing Stack Updates |
Previously Released; Omission of Data from Prior Patch Tuesday Data (5 CVEs)
| Released June 2024 | |
| CVE-2024-38213 | Bypass Vulnerability in Windows Mark of the Web |
| Released July 2024 | |
| CVE-2024-38165 | Tampering Vulnerability in Windows Compressed Folder |
| CVE-2024-38185 | Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Windows Kernel-Mode Driver |
| CVE-2024-38186 | Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Windows Kernel-Mode Driver | CVE-2024-38187 | Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Windows Kernel-Mode Driver |
Previously Released (Cloud); Data Offered as Notifications Only (3 items)
| CVE-2024-38109 | Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Azure Health Bot |
| CVE-2024-38166 | Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
| CVE-2024-38206 | Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Microsoft Copilot Studio |
Pertinent to Adobe (non-Microsoft release) (12 CVEs)
| APSB24-57 | CVE-2024-39383 | Usage After Release (CWE-416) |
| APSB24-57 | CVE-2024-39422 | Usage After Release (CWE-416) |
| APSB24-57 | CVE-2024-39423 | Writing Beyond Bounds (CWE-787) |
| APSB24-57 | CVE-2024-39424 | Usage After Release (CWE-416) |
| APSB24-57 | CVE-2024-39425 | Time-of-check Time-of-use (TOCTOU) Race Condition (CWE-367) |
| APSB24-57 | CVE-2024-39426 | Access After End of Buffer (CWE-788) |
| APSB24-57 | Memory Corruption (CWE-416) | |
| Bulletin ID: APSB24-57 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-41831 | Memory Corruption (CWE-416) |
| Bulletin ID: APSB24-57 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-41832 | Array Index Out-of-bounds (CWE-125) |
| Bulletin ID: APSB24-57 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-41833 | Array Index Out-of-bounds (CWE-125) |
| Bulletin ID: APSB24-57 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-41834 | Array Index Out-of-bounds (CWE-125) |
| Bulletin ID: APSB24-57 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-41835 | Array Index Out-of-bounds (CWE-125) |
Section E: List of Security Vulnerabilities Affecting CBL-Mariner / Azure Linux
The data regarding these security vulnerabilities, which come from various Certificate Authorities, often varies significantly from that provided for vulnerabilities covered in Microsoft’s regular security updates. Sometimes, there is missing information such as vulnerability titles or CVSS scores. In this table, we have opted to present the vulnerabilities as outlined in Microsoft’s official summary.
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2007-4559 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-36648 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-37370 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-40898 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2017-17522 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-3775 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-37371 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-40902 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2017-18207 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-3872 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-38428 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-41110 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2019-20907 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-4144 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-38571 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42068 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2019-3816 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-41722 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-38583 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42070 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2019-3833 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-48788 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-38662 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42071 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2019-9674 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-48841 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-38780 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42072 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2021-23336 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2023-29402 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39277 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42073 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2021-3750 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2023-29404 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39292 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42074 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2021-3929 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2023-3354 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39331 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42075 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2021-4158 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2023-45288 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39473 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42076 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2021-4206 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2023-52340 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39474 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42077 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2021-4207 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-0397 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39475 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42078 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2021-43565 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-0853 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39476 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42080 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-0358 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-2004 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39480 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42082 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-2601 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-23722 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39482 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42083 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-26353 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-2398 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39483 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-42237 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-26354 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-2466 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39484 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-6104 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-29526 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-26461 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39485 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-6257 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-2962 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-26900 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39489 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-6655 |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-3165 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-36288 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39493 | |
| Vulnerability ID: CVE-2022-35414 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-37298 | Vulnerability ID: CVE-2024-39495 |