
Definition of malware?
Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson talks about safeguarding yourself against malicious software and ransomware.
Proofpoint, an online security company, cautions against a new and advanced form of malicious software that poses as Google Chrome and Microsoft, presenting a potential threat to extract money from owners of devices using Windows. Various factions of cybercriminals are deploying this malicious software, including some renowned for disseminating unsolicited emails that can contaminate computers with malware or ransomware.
The malicious software masquerades as counterfeit updates in web browsers like Chrome to deceive users into downloading harmful code. Once the code infiltrates the computer, cyber attackers can gain access to cryptocurrencies, sensitive documents, and personal data.

Microsoft laptops (Microsoft) (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
What is the modus operandi of the phony update malicious software?
Proofpoint uncovered an extensive rollout of this malicious software this month, but the online security organization believes that the scheme has been operational since March 2024. The malicious software is disguised as fake Google Chrome, Word, and OneDrive glitches to coerce users into downloading malicious code. These glitches prompt the user to click a button to copy a PowerShell “solution” into the clipboard, then paste and execute it in a Run dialog box or PowerShell prompt.
Warning from Proofpoint, “Although the attack process necessitates significant user participation for successful execution, the social engineering is astute enough to present an individual with what resembles a genuine issue and resolution concurrently, compelling the user to act without evaluating the risk.”
Upon the execution of the PowerShell script, it validates if the device is a viable target. Subsequently, it initiates the download of additional payloads. These stages encompass clearing the DNS cache, eradicating clipboard content, displaying a deceptive message, and retrieving another external PowerShell script.
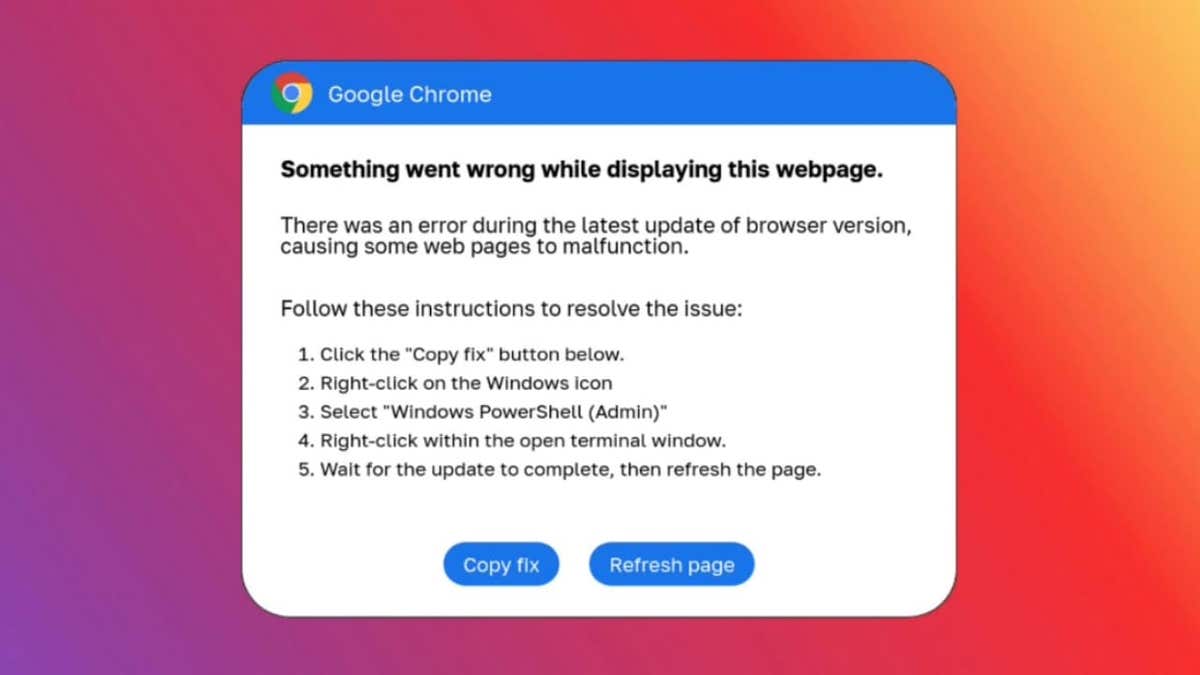
ClickFix error message (Proofpoint) (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
TOP ANTIVIRUS SOLUTIONS FOR PCS, MACS, IPHONES, AND ANDROIDS – CYBERGUY SELECTIONS
Cryptocurrency embezzlement
This successive script scrutinizes if it is operational on a virtual machine before installing an information thief. Once all prerequisites are fulfilled, the hacker can penetrate the victim’s cryptocurrency. This ploy diverts the victim’s funds to the hacker instead of the intended recipient.
Alternate method of attack: Email enticement
Proofpoint remarks that malevolent actors also employ an alternative technique known as “email lure” to embed detrimental software. Emails, often masquerading as work-related or corporate content, incorporate an HTML file resembling Microsoft Word. These emails prompt users to install the “Word Online” plug-in for proper document viewing.
Similar to the previous method, users are instructed to open PowerShell and transfer malicious code. According to Proofpoint, the deceptive “campaign” is pervasive. As per the organization, “The initiative encompassed over 100,000 correspondences and targeted multitude organizations worldwide.”
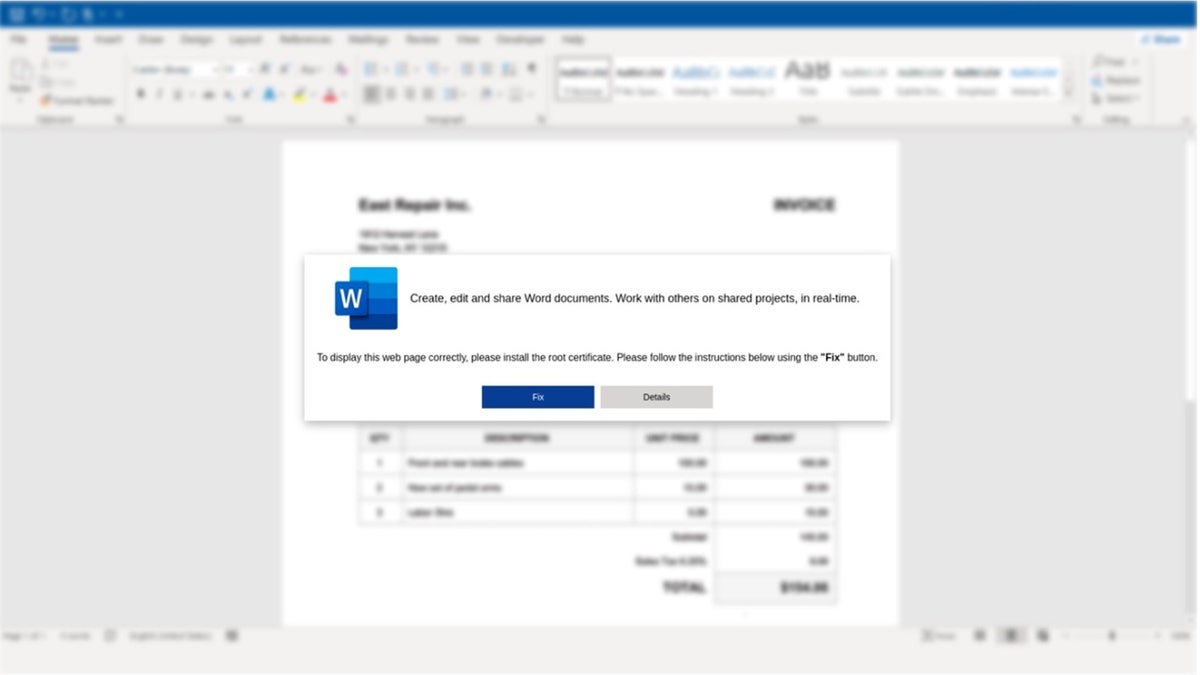
HTML attachment containing instructions on how to copy and paste PowerShell that leads to the installation of malware (Proofpoint) (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
PREVENT SNOOPS NEARBY FROM EAVESDROPPING ON YOUR VOICEMAIL WITH THIS PROMPT SUGGESTION
5 strategies to shield yourself from malevolent software
The misleading Chrome and Microsoft Word malware fabricates a sense of urgency, compelling users to click on the links and unknowingly endanger their devices. Implementing several precautions can safeguard you against such malicious software.
1) Have potent antivirus software: The most effective approach to shield yourself against clicking on malevolent links that install malware, thereby potentially compromising your private data, is to have antivirus shielding operational on all your gadgets. This can also notify you of any phishing emails or ransomware ploys. Explore my recommendations for the top 2024 antivirus protection frontrunners for your Windows, Mac, Android, and iOS devices.
2) Utilize a VPN: Delve into adopting a VPN to shield against tracking and to obfuscate your likely location on the websites you access. Numerous websites can discern your IP address and, depending on their privacy settings, could showcase the city from which you are corresponding. A VPN will camouflage your IP address to exhibit an alternative location. For premier VPN software, dissect my expert evaluation of the best VPNs for discreetly navigating the web on your Windows, Mac, Android, and iOS devices.
3) Administer account monitoring: Regularly scrutinize your bank statements, credit card statements, and other monetary accounts for any unauthorized actions. If any dubious transactions are detected, promptly report them to your financial institution or credit card provider.
4) Implement a fraud alert: Connect with one of the three major credit reporting agencies (Equifax, Experian, or TransUnion) and request the imposition of a fraud alert on your credit dossier. This will complicate identity thieves’ attempts to inaugurate new accounts under your identity sans authentication.
5) Activate two-factor authentication: Activate two-factor authentication wherever feasible. This introduces an extra tier of security by necessitating a second verification form, such as a code transmitted to your phone, coupled with your password.
PROCEDURE TO ELIMINATE YOUR CONFIDENTIAL DATA FROM THE INTERNET
Kurt’s principal insights
Cunningly crafted malware prompts the installation thereof on your gadgets. This malware specifically targets Windows users, and I’ve discerned that Windows devices appear to be more vulnerable to such attacks. Recently, Microsoft acknowledged a Wi-Fi driver vulnerability in Windows enabling hackers to seize control of your PC merely by being on the same Wi-Fi network. Vigilance while browsing online or connecting to public Wi-Fi is imperative.
How do you authenticate the genuineness of software prior to downloading and installing it on your device? Share your perspectives by reaching out to us at Cyberguy.com/Contact.
To stay updated on my tech tips and security advisories, subscribe to my complimentary CyberGuy Report Newsletter at Cyberguy.com/Newsletter.
Pose a query to Kurt or suggest stories you would like us to investigate.
Follow Kurt on his social media platforms
Answers to frequently asked questions about CyberGuy:
© 2024 CyberGuy.com. All rights reserved.





